Three marks
Define Economics? Why is the study of Economics useful for engineers?
Economics is a social science that studies how individuals, governments, firms, and nations make choices on allocating limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants.
-
Decision-making:
- Economics helps engineers make better choices by analyzing costs, benefits, and trade-offs.
-
Efficiency:
- Engineers can design more efficient solutions by understanding concepts like productivity and cost-effectiveness.
-
Cost analysis:
- Economics provides tools to assess the financial feasibility of projects and identify cost-saving opportunities.
-
Supply and demand:
- Understanding market dynamics helps engineers adapt designs to meet customer needs and optimize production and pricing strategies.
-
Project evaluation:
- Engineers can evaluate the financial viability of projects, considering revenue, costs, and market demand.
-
Innovation and entrepreneurship:
- Economic insights help engineers identify market opportunities, assess demand, and foster innovation.
What do you mean by Demand and Supply ?Explain the Law of Demand
Supply and demand are perhaps one of the most fundamental concepts of economics and it is the backbone of a market economy.
- Demand: The quantity demanded is the amount of a product people are willing to buy at a certain price.
- Supply: The quantity supplied refers to the amount of a certain goods producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price.
Law of Demand :
We have stated earlier that demand for a commodity is related to price per unit of time. It is the experience of every consumer that when the prices of the commodities fall, they are tempted to purchase more. Commodities and when the prices rise, the quantity demanded decreases.
There is, thus, inverse relationship between the price of the product and the quantity demanded. The economists have named this inverse relationship between demand and price as the law of demand.
Define Terms: 1. Economics 2.Personal Income 3. Interest Rate
- Economics : Economics is a social science that studies how individuals, governments, firms, and nations make choices on allocating limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants.
- Personal Income : Personal income is the money that individuals earn from various sources, like their jobs, investments, or business ventures. It includes wages, salaries, bonuses, dividends, and any other income received by individuals. Personal income helps measure how much money people have available to spend, save, or invest.
- Interest Rate : The interest rate is the percentage charged or earned on a loan or investment, representing the cost of borrowing or the return on an investment.
List the factors that influence elasticity.
- Availability of substitutes
- Type of goods whether it is a necessity or luxury
- Time
- Proportion of income spent
- Brand loyalty
- Durability and perishability
- Income level
Explain the type of cost briefly.
- Fixed Costs:
- Expenses that don't change with production or sales
- Examples: Rent, salaries, insurance
- Variable Costs:
- Expenses that change with production or sales
- Increase with higher production and decrease with lower production
- Examples: Raw materials, direct labor, sales commissions
- Total Costs:
- Sum of fixed costs and variable costs
- Represents overall expenses to produce a specific quantity
- Marginal Costs:
- Additional cost of producing one more unit
- Helps make decisions about production levels and pricing
- Average Costs:
- Total cost per unit of output
- Average fixed costs: Total fixed costs divided by quantity
- Average variable costs: Total variable costs divided by quantity
- Opportunity Costs:
- Value of the next best alternative forgone
- Represents the value of the alternative option that could have been chosen
What do you mean by break even point .what it indicate
- Break-even point is the level of sales or production where total revenue equals total costs.
- It represents the minimum level of activity needed to cover all costs.
- At the break-even point, a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss.
- It helps businesses assess their financial viability and make decisions about pricing and production levels.
- Sales above the break-even point result in profits, while sales below it lead to losses.
- It serves as a reference point for setting sales targets and evaluating profitability.
- Understanding the break-even point is crucial for cost management and planning for profitability.
What are the Primary and Secondary function of banks
Primary Functions:
- Acceptance of Deposits: Savings, current, fixed deposits, recurring deposits.
- Advances of Loans: Providing loans, overdrafts, cash credits.
Secondary Functions:
- Collection of Money: Collecting cheques, drafts, interest, dividends on behalf of customers.
- Payments of Money: Making payments to outside parties on behalf of clients.
- Internet Money Transfer and E-banking: Electronic transfer of funds and online banking services.
- Merchant Banking: Providing consultancy services for financial, marketing, and legal matters.
- Dematerialized Account Service: Electronic-based share market transactions and demat account services.
what do you mean contribution .how it differ from contribution ratio
The contribution is the difference between the sales and the variable cost.
- 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑏𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛=𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠−𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡𝑠
- 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑏𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛/𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡=𝑆𝑒𝑙𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒/𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡−𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡/𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡
Contribution:
- The amount of revenue that remains after subtracting variable costs.
- Represents the direct contribution towards covering fixed costs and generating profit.
- Expressed as a monetary value.
Contribution Ratio:
- The percentage of each unit's revenue that contributes towards covering fixed costs and generating profit.
- Calculated by dividing the contribution (revenue minus variable costs) by the revenue and multiplying by 100.
- Provides insights into the profitability and efficiency of a product or service.
- Expressed as a percentage.
‘Good planning is half work done.’ Explain
- Clear Direction:
- Planning provides a roadmap and defines objectives, giving a clear direction for achieving goals.
- Efficiency:
- Effective planning helps allocate resources efficiently, saving time, money, and effort.
- Minimizing Mistakes:
- Planning helps identify potential risks and challenges in advance, reducing the likelihood of mistakes or failures.
- Resource Optimization:
- Planning ensures resources are used optimally, avoiding wastage and unnecessary costs.
- Time Management:
- Planning helps prioritize tasks and manage time effectively, ensuring deadlines are met.
- Adaptability:
- Good planning includes flexibility to adapt to changes, allowing for proactive decision-making and adjustments.
List and Explain Characteristics of “Perfect Competition” type markets.
- Large number of buyers and sellers.
- No barriers to entry and exit.
- Perfect factor mobility.
- Perfect information/knowledge.
- Zero transaction costs.
- Profit maximization.
- Homogeneous products.
- Non-increasing returns to scale.
- Property rights.
- Rational buyers.
- A large number buyers and sellers : A large number of consumers with the willingness and ability to buy the product at a certain price, and a large number of producers with the willingness and ability to supply the product at a certain price.
- No barriers to entry and exit : No entry and exit barriers make it extremely easy to enter or exit a perfectly competitive market.
“Inflation is an unaccounted Tax on citizens”, is it True? Justify your answer with suitable arguments.
- Decreased Purchasing Power:
- Inflation reduces the value of money over time, causing prices to rise and citizens needing more money to buy the same goods and services.
- Redistribution of Wealth:
- Inflation can lead to a redistribution of wealth, benefiting those with assets while negatively impacting individuals with fixed incomes.
- Hidden Impact on Savings:
- Inflation erodes the value of savings over time, reducing the future purchasing power and financial security of citizens.
- Cost-Push Inflation:
- Increased production costs can cause businesses to raise prices, passing the burden onto consumers and effectively acting as an additional financial burden.
- Economic Distortions:
- High inflation rates create uncertainty and volatility, which can hinder economic growth, employment opportunities, wages, and overall stability.
What is role of Central Bank in economy of a nation?
- Monetary Policy:
- Formulating policies to manage money supply, interest rates, and credit conditions for economic stability and growth.
- Currency Issuance:
- Authority to issue and regulate the country's currency, ensuring stability and adequate supply.
- Banker to the Government:
- Providing banking services, managing government accounts, and assisting with debt issuance.
- Supervision and Regulation:
- Overseeing and regulating the banking and financial system for stability and soundness.
- Lender of Last Resort:
- Providing emergency liquidity support during financial crises to prevent disruptions.
- Foreign Exchange Management:
- Managing foreign exchange reserves and policies to maintain stability and manage currency fluctuations.
- Economic Research and Analysis:
- Conducting research and analyzing economic indicators for informed policy decisions.
- Financial Stability:
- Monitoring systemic risks and implementing measures to promote stability in the financial system.
- Payment Systems and Settlements:
- Overseeing payment systems for smooth and efficient financial transactions.
Differentiate Management and Administration.
Define management. Compare management and administration(winter-3)
Differentiate between Management and Administration.(winter-3)
- Management involves coordinating and supervising activities to achieve goals efficiently and effectively.
- Efficiency means using resources wisely and minimizing waste and unnecessary effort.
- Effectiveness refers to doing the right things that help the organization reach its goals.
| Heading | Management | Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Art of getting things done through others by directing their efforts towards achievement of predetermined goals. | Decision-making function concerned with formulation of objectives, plans, and policies. |
| Characteristics | Executing/implementing function. | Decision-making function. |
| Process | Decides who will do it and how it will be done. | Decides what is to be done and when it is to be done. |
| Purpose | Main function is to get work done through others. | Main purpose is to frame plans and policies. |
| Skill | Requires technical and human skills. | Requires conceptual and human skills. |
| Level | Middle and lower level function. | Top level function. |
What is the importance of Human Resource Management?
- Strategic Alignment:
- HRM ensures that the workforce supports the organization's strategic goals.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention:
- HRM attracts and retains skilled employees.
- Employee Development:
- HRM enhances employees' skills and abilities through training and development.
- Performance Management:
- HRM evaluates and improves employee performance for increased productivity.
- Employee Engagement:
- HRM creates a positive work environment that boosts employee satisfaction.
- Compliance and Risk Management:
- HRM ensures legal compliance and minimizes employment-related risks.
- Organizational Culture:
- HRM shapes a positive company culture that promotes collaboration and well-being.
- Change Management:
- HRM supports employees during organizational changes.
- Conflict Resolution:
- HRM addresses conflicts and maintains a harmonious work environment.
- Compensation and Benefits:
- HRM designs competitive compensation packages to motivate employees.
How CSR can provide benefits to society?
Certainly! Here are five key ways in which CSR can benefit society, explained in simple language:
- Social Impact:
- CSR initiatives address social issues and contribute to the well-being of society, such as education, healthcare, poverty alleviation, and community development.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- CSR promotes sustainable practices, reduces ecological impact, and preserves natural resources for future generations.
- Economic Development:
- CSR creates job opportunities, supports local economies, and encourages fair trade practices and entrepreneurship.
- Innovation and Research:
- CSR initiatives often drive innovation, research, and development of sustainable solutions and technologies that can benefit society and address societal challenges.
- Ethical Business Practices:
- CSR promotes responsible and ethical behavior, ensuring transparency, fairness, and integrity in business operations, which builds trust and a positive reputation.
Define Economics. Compare Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Economics is a social science that studies how individuals, governments, firms, and nations make choices on allocating limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants.
| Aspect | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Studies individual economic units like households and firms. | Studies the economy as a whole. |
| Scope | Focuses on specific markets, prices, and individual economic decisions. | Focuses on overall economic indicators and trends. |
| Analysis | Examines individual choices and market interactions. | Analyzes aggregate economic variables and their relationships. |
| Factors | Considers individual preferences, supply, demand, and market equilibrium. | Considers factors like GDP, inflation, unemployment, and government policies. |
| Perspective | Zooms in on specific economic units and their behaviors. | Looks at the overall performance and trends of the economy. |
| Policy | Influences micro-level policies such as price controls and regulations. | Influences macro-level policies like fiscal and monetary policies. |
| Examples | Study of consumer behavior, firm production, and market structures. | Analysis of GDP, inflation rate, unemployment rate, and economic growth. |
Define: 1. Opportunity Cost. 2. Sunk Cost. 3. Margin of Safety.
Certainly! Here are simplified definitions of the terms:
- Opportunity Cost:
- Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is forgone when making a choice. It represents what you give up in terms of benefits or gains when you choose one option over another.
- Sunk Cost:
- A sunk cost is money or resources that have already been spent and cannot be recovered. Once a cost is sunk, it is irrelevant to future decision-making because you can't change or get it back.
- Margin of Safety:
- The margin of safety is the difference between the actual or current level of performance and the level at which you break even or achieve your desired goals. It provides a buffer or cushion to handle unexpected changes or risks, ensuring profitability or avoiding losses. It helps protect against uncertainty and allows for a safety net in business operations.
Define the term production and explain any two factors of production.
Production refers to the process of turning inputs into desired goods or services. Two factors of production are:
- Labor:
- The physical and mental efforts of workers. It includes their skills, knowledge, and expertise.
- Capital:
- Physical assets used in production, like machinery, equipment, and buildings.
- Land:
- Natural resources used in production, such as minerals, water, and agricultural land.
- Entrepreneurship:
- Combining and organizing the other factors of production, taking risks, and making strategic decisions.
These factors work together to create products efficiently. By understanding and using them effectively, businesses can optimize production and achieve growth.
Write about the various types of Banks. Explain in brief.
- Scheduled Banks are a category of banks listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. They can be further classified into commercial and cooperative banks. Here's a brief explanation of the different types of scheduled banks:
-
Scheduled Commercial Banks:
- Public Sector Banks: Owned and operated by the government. Examples: SBI, BOB, PNB, Canara Bank, etc.
- Private Sector Banks: Owned and operated by private institutions. Examples: ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, Axis Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, etc.
- Regional Rural Banks: Provide credit to rural and agricultural areas. Examples: Saurashtra Gramin Bank, Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank, etc.
- Foreign Banks: Registered in their home country, with branches in India. Examples: HSBC, Standard Chartered Bank, City Bank, etc.
-
Scheduled Cooperative Banks:
- Cooperative Banks: Controlled, owned, and operated by cooperative societies. Examples: The Kalupur Commercial Cooperative Bank Ltd., Rajkot Nagrik Sahkari Bank Ltd., etc.
- Scheduled banks play a significant role in the Indian banking system, providing financial services and support to individuals, businesses, and communities.
Define the following terms: Management, Marketing, and Money.
- Management:
- Management is the process of overseeing and coordinating activities in an organization to achieve goals.
- Marketing:
- Marketing involves identifying, satisfying, and communicating with customers to create value and generate sales.
- Money:
- Money is a widely accepted medium of exchange used to buy goods and services, measure value, and store wealth.
Explain the relationship between Total, Fixed and Variable costs.
- Total costs: Total costs are the sum of all expenses in the production of goods or services.
- Fixed costs: Fixed costs do not change with production or sales volume and remain constant.
- Variable costs: Variable costs fluctuate based on production or sales volume.
- Relationship: Total costs are the combination of fixed costs and variable costs.
- Increase in Production: As production or sales volume increases, variable costs increase proportionally, leading to an increase in total costs.
- Fixed Costs Remain Constant: Fixed costs do not change regardless of the level of production or sales.
- Impact on Total Costs: The relationship between total, fixed, and variable costs depends on the level of production or sales volume.
Define economics and explain the scope of economics.
- Economics is the study of how people, businesses, governments, and societies make choices to use limited resources to meet their unlimited needs and wants. It examines how goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed.
- Microeconomics:
- Studies choices in production, consumption, prices, supply and demand, market structures, and resource allocation.
- Macroeconomics:
- Focuses on the overall economy, analyzing factors like national income, unemployment, inflation, economic growth, and government policies.
- Economic Systems:
- Examines different systems (capitalism, socialism, mixed economies) and the role of government, markets, and property rights in resource allocation and production.
- Public Economics:
- Analyzes the government's role, studying public goods, taxation, spending, and their impact on resource allocation and economic well-being.
- International Economics:
- Studies interactions between countries, including trade, exchange rates, finance, global organizations, and the impact of globalization.
- Development Economics:
- Explores conditions and strategies for growth, poverty reduction, income distribution, and the role of institutions and policies in less affluent countries.
What are the different concepts of Marketing?
Different Concepts of Marketing:
- Production Concept:
- Focuses on efficient production and distribution of affordable products.
- Product Concept:
- Emphasizes quality and unique features of the product.
- Selling Concept:
- Assumes aggressive sales and promotion are needed to drive customer purchases.
- Marketing Concept:
- Puts customer needs at the center, aims to deliver superior value.
- Societal Marketing Concept:
- Considers ethical, environmental, and social factors in marketing decisions.
- Relationship Marketing:
- Focuses on building long-term customer relationships.
- Digital Marketing:
- Uses digital channels for marketing efforts, such as websites and social media.
- Integrated Marketing:
- Coordinates various marketing channels for a consistent customer experience.
Refactor with smaller sentences, point to point, and easy language.
Q.6 (a) Define: 1. Business Ethics. 2. Inflation. 3. Net Demand and time liabilities (NDTL).
- Business Ethics:
- Business ethics refers to the moral principles and values that guide how individuals and organizations behave in the business world.
- Inflation:
- Inflation is the ongoing increase in the overall prices of goods and services in an economy over time, which reduces the purchasing power of money.
- Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL):
- NDTL is a term used in banking to describe the total deposits in a bank that can be withdrawn immediately (demand liabilities) or after a specified period (time liabilities).
Refactor with smaller sentences, point to point, and easy language.
Define: 1. Corporate Governance. 2. Human Resource Management. 3. Organization.
- Corporate Governance:
- Corporate governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. It involves balancing the interests of various stakeholders and ensuring transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior in managing the organization.
- Human Resource Management:
- Human Resource Management (HRM) is the function within an organization that focuses on managing and maximizing the potential of its employees. It involves activities such as recruitment, selection, training, performance management, compensation, and employee relations to ensure the organization has a skilled and motivated workforce.
- Organization:
- An organization is a structured entity that consists of individuals working together towards a common goal. It involves the arrangement of people, resources, and processes to achieve specific objectives. Organizations can be for-profit businesses, non-profit organizations, government agencies, or other types of entities.
Explain Role and Functions of RBI.
- Monetary Authority:
- The RBI formulates and implements monetary policies to control inflation and maintain price stability.
- Banker to the Government:
- It manages the government's bank accounts, conducts transactions, and provides loans when needed.
- Banker's Bank and Supervisor:
- The RBI serves as the banker to commercial banks and regulates their activities to ensure stability and consumer protection.
- Currency Issuance:
- It has the authority to issue currency notes, except for one-rupee notes, and maintains the supply of currency.
- Monetary Policy Implementation:
- The RBI implements policies set by the Monetary Policy Committee to control money supply and influence interest rates.
- Financial Market Regulation:
- It regulates and supervises financial markets to promote transparency and efficiency.
- Developmental Functions:
- The RBI promotes financial inclusion, digital payments, and the growth of MSMEs. It focuses on financial literacy and consumer protection.
- Foreign Exchange Management:
- It manages and regulates foreign exchange transactions and reserves, ensuring exchange rate stability.
- Data Collection and Research:
- The RBI collects and publishes economic and financial data, conducts research, and provides insights.
- International Relations:
- The RBI represents India in international forums, collaborates with other central banks, and addresses global economic challenges.
These functions help maintain monetary stability, promote financial sector development, and ensure the stability of the Indian financial system.
Explain about different types of money.
Types of Money:
-
Physical Form:
- Metallic Money: Coins made of metal, such as 25 Paisa, 50 Paisa, and 1 Rupee.
- Paper Money: Currency notes printed on special paper, like Rs. 10, Rs. 100, Rs. 500, and Rs. 1000.
- Plastic Money: Cards issued by recognized institutes, including credit cards, debit cards, and travel cards.
-
Money Creation:
- Narrow Money (Fiat Money) (M1): Coins and currencies introduced by the central bank to facilitate exchange. Created by the central bank, like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Wide Money (Broad Money) (M2): Credit money, including fixed deposits, credit notes, and demand drafts. Created by the banking system based on the circulating currency.
-
Legal Force:
- Legal Money: Coins and currencies introduced by the central bank, known as legal tender or legal currency.
- Optional Money: Instruments like cheques, pay orders, and bills of exchange issued by reputable individuals and institutions. Acceptance can be refused if the issuer's creditworthiness is in doubt.
-
Accounting:
- Cash System: Transactions recorded using coins and currencies.
- Accrual System: Non-cash considerations accounted for as incomes and expenses to determine accounting profits. Non-cash incomes are accrued but not received, while non-cash expenses are accrued but not paid in cash.
Management is an art. Justify the statement.
Management is considered an art due to the following reasons:
- Creativity:
- Managers use creative thinking to find innovative solutions and strategies.
- Skill Development:
- Managers improve their abilities through practice and experience.
- Subjectivity:
- Managers make judgments based on their interpretations and understanding.
- Personal Style:
- Managers develop their unique approaches and leadership styles.
- Expression of Vision:
- Managers have a vision for their organization and work to make it a reality.
- Continuous Learning:
- Managers continuously learn and adapt to changing circumstances.
These aspects of creativity, skill development, subjectivity, personal style, expression of vision, and continuous learning contribute to management being classified as an art.
Define the following terms: reverse repo rate, repo rate, bank rate
Define the following terms: bank rate, repo rate,& reverse repo rate
- Bank Rate:
- The rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks.
- Repo Rate:
- The rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks against government securities.
- Reverse Repo Rate:
- The rate at which the central bank borrows money from commercial banks against government securities.
Discuss the stock and flow concept of national income?
- The stock concept of national income refers to the accumulated wealth or assets held by individuals, businesses, and the government at a particular point in time.
- It includes physical assets like buildings, machinery, and financial assets like stocks, bonds, and savings.
- The flow concept of national income, on the other hand, refers to the income generated from economic activities during a specific period, typically a year.
- It includes wages, salaries, profits, rent, and other forms of income earned by individuals and businesses.
- The stock represents the existing wealth in an economy, while the flow represents the ongoing economic activity that generates income and contributes to the overall national income.
Explain perfect competition with suitable example.
- Perfect competition is a market structure with many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, perfect information, easy entry and exit, and no control over prices.
- In perfect competition, firms are price takers and have no influence on the market price.
- An example of perfect competition is the agricultural market for a standardized commodity like wheat.
- Farmers in this market produce identical wheat crops and must sell at the prevailing market price.
- Buyers have perfect information and can easily switch between sellers based on price and quality.
- There are no barriers to entry or exit in perfect competition.
- Supply and demand determine the market price, and firms compete on price and quality.
- Each firm operates as a price taker and aims to maximize profits by optimizing production and minimizing costs.
What is difference between absolute and relative poverty?
| Aspect | Absolute Poverty | Relative Poverty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed poverty line for basic needs | Poverty compared to others in society |
| Threshold | Constant, doesn't change with location | Varies based on society's income |
| Focus | Meeting essential needs (food, shelter) | Income inequality and disparities |
| Timeframe | Long-term measure | Can change with societal changes |
| Economic Growth | Not affected by economic growth | Can be influenced by income distribution |
| Comparison | Independent of others' incomes | Compared to others' incomes |
| Universality | Same for all countries | Varies across societies |
| Policy Implications | Addresses basic needs | Focuses on reducing inequality |
How does culture affects managers and employees?
Culture has a significant impact on managers and employees in an organization. Here's how it affects them:
- Communication:
- Culture influences how managers and employees communicate with each other, including the style and formality of communication.
- Decision-Making:
- Cultural values shape the decision-making process, whether it involves seeking consensus or relying on hierarchical decision-making.
- Leadership:
- Culture plays a role in leadership styles and expectations, such as authoritative, participatory, or democratic leadership.
- Work Ethic:
- Cultures have different attitudes towards work, emphasizing individual achievement or collective effort and harmony.
- Organizational Values:
- Culture shapes the core values and beliefs of an organization, influencing how managers and employees perceive their roles and work environment.
By understanding and respecting cultural differences, managers can create a positive and inclusive work culture that enhances employee engagement and collaboration.
Discuss role and skills of a Manager.
Roles of a Manager:
-
Interpersonal Role: a. Figurehead: Represents the organization and performs formal duties. b. Leader: Motivates and directs subordinates, sets goals, and solves work-related problems. c. Liaison: Establishes connections between the organization and outsiders.
-
Informational Role: a. Monitor: Establishes and maintains information systems, collects and analyzes information. b. Disseminator: Shares external and internal information with relevant stakeholders.
-
Decisional Role: a. Entrepreneur: Identifies opportunities, initiates changes, and takes risks. b. Disturbance Handler: Manages crises and resolves conflicts. c. Resource Allocator: Allocates resources to achieve organizational goals. d. Negotiator: Represents the organization in negotiations and resolves conflicts.
Skills of a Manager:
- Leadership:
- Inspires and guides employees to achieve goals.
- Communication:
- Effectively conveys information and listens to others.
- Decision-making:
- Analyzes situations and makes informed choices.
- Problem-solving:
- Identifies and resolves problems in the workplace.
- Time management:
- Efficiently manages tasks and prioritizes work.
- Adaptability:
- Adapts to changing situations and embraces new ideas.
- Networking:
- Builds and maintains relationships with internal and external stakeholders.
- Technical expertise:
- Possesses knowledge and skills specific to the industry or field.
By performing these roles and utilizing their skills, managers contribute to the success of the organization and create a positive work environment for their employees.
Four marks
Differentiate between macro and micro economics in brief.
Differentiate between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Differentiate Microeconomics & Macroeconomics with their significance in assessing Economies.
| Aspect | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Examines individual economic agents | Studies the entire economy as a whole |
| Focus | Behavior of households, firms, and industries | Aggregates the behavior of all economic agents |
| Variables | Micro-level variables (e.g., prices, supply and demand, individual consumer choices) | Macro-level variables (e.g., GDP, inflation, unemployment rate) |
| Analysis | Concerned with specific markets and industries | Concerned with overall economic performance and policies |
| Interactions | Focuses on individual market interactions | Focuses on interrelationships between markets |
| Goal | Maximization of individual utility and profit | Stable economic growth and full employment |
| Examples | Study of supply and demand for a specific product | Analysis of national income and output |
| Policy Implications | Influences decision-making of individual firms and households | Influences government policies and regulations at the national level |
Discuss the meaning and functions of money in detail. (Winter-7)
Explain characteristics and function of money.
What is money? List and Explain various characteristics of money.
Meaning of Money:
- Money is a term derived from the Latin word "Moneta," which refers to an accepted medium of transfer. It encompasses coins or currency notes that are widely acknowledged as a medium of exchange between parties engaged in transactions.
Characteristics of Money:
- Durability: Money should be able to withstand physical wear and tear, ensuring its usability over a prolonged period.
- Portability: Money needs to be easily carried from one place to another, enabling individuals to conduct transactions conveniently.
- Divisibility: Money should be divisible into smaller denominations, allowing for flexible transactions of varying values (such as rupees and paisa).
- Uniformity: Money should possess uniformity in terms of its appearance, making it easy to count, identify, and measure accurately.
- Limited Supply: The supply of money should be controlled by a central authority, ensuring its stability and preventing excessive issuance.
- Acceptability: Money must be universally accepted within an economy, enabling individuals to exchange it for goods and services without complications.
- Recognizability: Money should be easily identifiable, distinguishable, and measurable, ensuring its authenticity and credibility in transactions.
Discuss functions of Money
Functions of Money:
-
Medium of Exchange:
- Money is a widely accepted instrument used to buy goods and services.
- It allows for easy transactions, eliminating the need for bartering or direct exchange.
- Compared to the barter system, money is a more efficient medium of exchange.
-
Measure of Value:
- Money serves as a standard unit of account for measuring the value of goods, services, and transactions.
- It provides a common standard for pricing and comparing different items.
- A unit of account is necessary for commercial agreements involving debt.
-
Standard of Measure:
- Money acts as a standard measure and a common denomination for trade.
- It provides a basis for quoting and bargaining prices.
- Efficient accounting systems rely on money as a standard of measure.
-
Store of Value:
- Money acts as a store of value, allowing individuals to save and accumulate wealth.
- It provides a relatively stable and liquid form of storing wealth.
- Money offers security for unforeseen emergencies and the ability to pay fixed debts.
- It allows individuals to take advantage of future buying opportunities.
- money functions as a medium of exchange, a measure of value, a standard of measure, and a store of value. It enables the smooth flow of transactions, facilitates economic calculation, supports trade and pricing, and provides a means to save and accumulate wealth.
An Automobile company wants to setup a new vehicle manufacturing plant in a particular region. List and Explain the various parameters which can influence unit cost of a car.
-
Local Labor Costs: The cost of labor in the region, including wages, benefits, and labor regulations, can impact the unit cost. Higher labor costs can increase overall expenses.
-
Availability of Raw Materials: The availability and proximity of raw materials needed for car manufacturing in the region can affect costs. Access to local suppliers can reduce transportation and logistics expenses.
-
Infrastructure and Utilities: The quality and cost of infrastructure, such as transportation networks, energy supply, and water resources, can impact the unit cost. Reliable and affordable utilities are crucial for efficient production.
-
Government Incentives and Regulations: Government policies, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and regulations, can influence manufacturing costs. Favorable policies can reduce expenses and make the region more attractive for investment.
-
Transportation and Logistics: The region's transportation infrastructure and proximity to major markets can affect transportation and logistics costs. Being closer to customers or having efficient distribution channels can lower expenses.
-
Exchange Rates: If the region's currency is subject to exchange rate fluctuations, it can impact the cost of imported components or raw materials. Currency stability is important for cost predictability.
-
Skilled Workforce: The availability of a skilled workforce with relevant expertise in automotive manufacturing can impact labor costs and productivity. Regions with well-trained workers may have an advantage.
-
Environmental Regulations: Environmental regulations imposed by the region can affect the unit cost. Compliance with stricter environmental standards may require additional investments or processes.
-
Supplier Networks: The presence of a robust supplier network in the region can reduce procurement costs. Access to local suppliers can provide cost efficiencies and faster response times.
-
Market Demand: The region's market demand for cars can influence the unit cost. Higher demand can lead to economies of scale and cost savings through increased production volumes.
What are the causes and remedies of unemployment?
What are the causes and remedies of unemployment?
Causes of Unemployment:
-
Slow rate of economic growth: Economic growth has been relatively slow compared to population growth, resulting in limited employment opportunities.
-
Preference for capital-centric production techniques: Investments have been primarily focused on capital-intensive techniques, leading to less reliance on human labor.
-
Defective education system: The education system often fails to equip students with the necessary skills demanded by industries, resulting in a skill gap and unemployment.
-
Lack of skill development opportunities: Insufficient availability of skill development programs and training hinders individuals from acquiring the necessary skills for employment.
-
Lack of manpower planning: Inadequate planning for the allocation of manpower among sectors can create imbalances, with some sectors having excess labor supply while others face shortages.
-
Limited labor mobility: People's reluctance to move to different regions for job opportunities limits their employment options.
-
Rapid population growth: The fast-growing population poses a challenge in generating enough jobs to accommodate the increasing workforce.
Remedies to Resolve Unemployment:
-
Accelerating economic growth rate: Promoting economic growth through planned development and investment can lead to increased employment opportunities.
-
Change in pattern of investment: Encouraging the adoption of labor-intensive technologies in both rural and urban sectors can generate more employment opportunities.
-
Employment-oriented planning: The organized industrial sector should absorb a sufficient number of workers by using labor-friendly technologies.
-
Role of employment exchange: Establishing more employment exchanges and disseminating information about job opportunities can help individuals find suitable employment.
-
Appropriate labor policies: Implementing flexible labor laws, providing access to finance for small enterprises, and removing bureaucratic obstacles can stimulate job creation.
-
Encouragement to self-employment: Supporting self-employment initiatives through financial assistance, training, and market access can create entrepreneurial opportunities.
-
Reform of the education system: Revamping the education system to include vocational training and industrial education can align skills with industry demands.
-
Control of population growth: Implementing effective family planning programs can help manage population growth and reduce unemployment pressure.
What is the meaning of Inflation? State the measures to be taken to control it
What should be the preparation to reduce inflation?
Inflation:
Definition:
- Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. It means OR Inflation refers to a continuous increase in the overall price level of goods and services.
- It is measured as a percentage increase over a year.
- Inflation reduces the purchasing power of money, meaning that the value of a rupee decreases as prices rise.
Measures to Control Inflation:
Monetary Measures (Controlled by the Central Bank):
- Credit Control: The Central Bank can limit the money supply in the market, which helps reduce inflation.
- Limiting New Currency Issuance: Restricting the issuance of new currency helps prevent further inflation.
- Increasing Bank Rate: Raising the interest rate charged to other banks limits their borrowing and reduces money supply in the market.
- Increasing Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): Requiring banks to keep a higher percentage of their deposits with the Central Bank reduces money supply.
- Increasing Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): Requiring banks to hold a higher percentage of their assets in the form of cash or approved securities limits money flow in the market.
- Open Market Operations (OMO): The Central Bank can sell government assets to reduce money supply in the economy.
Fiscal Measures (Controlled by the Government):
- Reduction in Public Expenditure: Cutting government spending reduces deficit-financing and decreases money supply in the economy.
- Increased Taxation: Imposing higher taxes collects more money from the economy, reducing demand.
- Tax Incentives on Savings and Investments: Introducing schemes that offer tax benefits for savings and investments encourages people to save and invest more.
- Extension of Repayment of Public Debt: Extending the repayment period for public debt helps reduce the immediate burden on the economy.
Other Measures:
- Price Control Strategy: Implementing price controls can help ensure essential goods remain affordable for the general population.
- Rationing: Introducing rationing systems can provide basic products at lower prices, enabling everyone to afford them.
- Increasing Production: Meeting the demand of the economy through increased production can stabilize prices and reduce inflation.
What is difference between absolute and relative poverty?
| Aspect | Absolute Poverty | Relative Poverty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of basic necessities for survival | Economic standing relative to the rest of society |
| Measurement | Based on a fixed and minimal standard of living | Compares income or wealth to average or median |
| Focus | Basic needs such as food, shelter, healthcare | Income or resources compared to the population |
| Threshold | Defined by income levels or consumption patterns | Defined by income or wealth distribution |
| International Standard | e.g., World Bank sets the poverty line at $1.90/day | Varies across countries and regions |
| Objective | Address extreme deprivation and basic human needs | Examine income inequality and social disparities |
Define “Organization.” Explain types of organization.
Definition of "Organization":
- An organization refers to a structured and coordinated entity that consists of people, resources, and systems working together to achieve specific goals or objectives. It is characterized by a defined structure, hierarchy, and division of tasks and responsibilities.
Types of Organizations:
-
For-profit Organizations:
- Sole Proprietorship: A business owned and operated by a single individual.
- Partnership: A business owned and operated by two or more individuals who share profits and responsibilities.
- Corporation: A legal entity separate from its owners, with shareholders who own shares of the company.
-
Non-profit Organizations:
- Non-governmental Organizations (NGOs): Organizations that operate independently from the government and focus on social, environmental, or humanitarian causes.
- Charitable Organizations: Organizations dedicated to promoting charitable or philanthropic activities, often for the public benefit.
- Foundations: Organizations that provide funding and support to various causes and projects.
-
Government Organizations:
- Federal, State, and Local Government Agencies: Organizations that operate at different levels of government and are responsible for public administration and governance.
- Public Institutions: Organizations such as schools, hospitals, and public libraries that are funded and operated by the government.
-
International Organizations:
- United Nations (UN): An intergovernmental organization that promotes cooperation among nations on various global issues.
- World Bank: An international financial institution that provides loans and financial assistance to developing countries.
- International Non-governmental Organizations (INGOs): Organizations that operate globally and address issues such as human rights, environmental protection, and development.
-
Professional Associations:
- Trade Associations: Organizations that represent and support businesses or professionals within a specific industry.
- Professional Societies: Organizations that bring together individuals working in a particular profession or field to share knowledge and promote professional development.
-
Social and Community Organizations:
- Community-based Organizations (CBOs): Organizations that address local issues and work to improve the well-being of a specific community.
- Social Clubs: Organizations formed around common interests or activities, such as sports clubs, hobby groups, or recreational organizations.
What is the difference between administration and management?
| Aspect | Administration | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of organizing and coordinating resources, people, and activities to ensure the smooth functioning and operation of an organization. | Planning, organizing, directing, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals and objectives. |
| Scope | Broader scope, encompassing the entire organization. | Narrower scope, focusing on specific departments, teams, or functions within the organization. |
| Level of Authority | Hold higher-level positions and have authority to make important decisions that affect the organization's overall direction, policies, and long-term goals. | Operate at different levels within the organizational hierarchy and have authority to make decisions within their assigned areas. |
| Timeframe | Focus on long-term planning and establishing frameworks that guide the organization's actions over an extended period. | Focus on short- to medium-term goals and activities necessary for day-to-day operations. |
| Responsibilities | Set the vision, provide guidance, strategic planning, policy development. | Implement plans, coordinate activities, supervise employees, ensure efficient operations. |
Differentiate the perfect competition and monopolistic competition.
Compare and Contrast Monopoly and Perfect Competition markets.
| Aspect | Monopoly Market | Perfect Competition Market |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Firms | Single firm dominates the market | Large number of firms exist in the market |
| Entry and Exit | Barriers to entry are high, limiting new firms from entering the market | Easy entry and exit for firms in the market |
| Product Differentiation | The firm sells unique products or services | Homogeneous products or services |
| Market Power | Monopolistic firm has substantial market power | No individual firm has market power |
| Price Determination | Monopolist has control over pricing and sets higher prices | Prices are determined by market forces (supply and demand) |
| Quantity Produced | Monopolist may limit quantity to maximize profits | Each firm produces a small portion of total market output |
| Competition | Limited or no competition | Intense competition among firms |
| Information | Monopolist has more information about market conditions | Information is freely available to all market participants |
| Profit Maximization | Monopolist aims to maximize profit | Firms compete to achieve optimal profit levels |
| Efficiency | May result in lower efficiency due to lack of competition | Promotes efficiency through competitive pressures |
“World is a global village”, is it true? Justify in terms of economic activities.
- Yes, the statement "The world is a global village" can be justified in terms of economic activities:
-
Global Trade:
- Countries now trade more freely with each other, exchanging goods and services.
- Businesses can sell their products to customers around the world, expanding their market reach.
- Trade agreements between countries encourage cooperation and boost economic growth.
-
International Supply Chains:
- Companies use materials and services from different countries to make products more efficiently.
- Parts of a product may be made in different countries and then assembled together.
- Collaboration between companies in different countries is important for supply chain success.
-
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- Companies invest in other countries to expand their operations and access new markets.
- Investments from foreign companies can create jobs and stimulate economic development.
- Countries benefit from the transfer of technology and knowledge brought by foreign investors.
-
Cross-Border Financial Transactions:
- Banks and financial institutions help move money across borders for investments and business transactions.
- People can easily transfer money to family members in other countries.
- Economic events in one country can affect financial markets worldwide.
-
Global Labor Market:
- People can find work opportunities in different countries, bringing their skills and expertise.
- Migrant workers often send money back to their home countries, boosting the local economy.
- Companies can hire talent from around the world to meet their workforce needs.
-
Technology and Communication:
- The internet and digital tools allow people to communicate and work together across borders.
- Online shopping enables consumers to buy products from anywhere in the world.
- Technology makes it easier for businesses to connect with customers globally.
-
Economic Interdependence:
- Economic changes in one country can impact other countries through trade and investments.
- Countries must work together to address global economic challenges, such as financial crises.
- Cooperation among nations is important for achieving stable and sustainable economic growth.
Discuss 4 P’s of Marketing.
- Product:
- Refers to the tangible or intangible offerings that a business provides to satisfy customer needs or wants.
- Involves determining product features, design, quality, packaging, and branding to create value for customers.
- Focuses on differentiation from competitors and ensuring the product meets customer expectations.
- Price:
- Represents the monetary value assigned to a product or service.
- Involves setting prices that align with customer perceptions of value and are competitive in the market.
- Factors such as costs, pricing strategies, discounts, and pricing flexibility are considered when determining the appropriate price.
- Promotion:
- Refers to the activities and communication strategies used to create awareness and generate demand for a product or service.
- Involves advertising, public relations, sales promotions, personal selling, and digital marketing to reach the target audience.
- Aims to communicate the benefits and value of the product, persuade customers, and build brand awareness.
- Place:
- Focuses on making the product available to customers at the right time and in the right location.
- Involves decisions related to distribution channels, such as direct sales, retail stores, e-commerce, or wholesalers.
- Considers factors like inventory management, transportation, logistics, and ensuring the product reaches the target market efficiently.
Compare role of Leader, Administrator, and Manager in organization.
NOTE: it's for 7 marks by length, so read accordingly
| Aspect | Leader | Administrator | Manager |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inspires and motivates individuals towards common vision and goals. | Handles administrative tasks and ensures efficient functioning of the organization. | Plans, organizes, and coordinates resources to achieve specific objectives and targets. |
| Focus | People-oriented, guiding and influencing others. | Process-oriented, implementing policies and procedures. | Task-oriented, achieving goals and driving results. |
| Decision-Making | Involved in strategic decision-making and setting vision. | Involved in decision-making related to resource allocation. | Involved in operational decision-making and task delegation. |
| Communication | Communicates vision, values, and goals to inspire employees. | Communicates policies, procedures, and guidelines. | Communicates objectives, tasks, and expectations to employees. |
| Role in Change | Champions change initiatives, encourages innovation. | Implements and manages change processes and transitions. | Drives change through planning, organizing, and executing strategies. |
| Relationship | Builds relationships, mentors employees, fosters positive work culture. | Provides support and guidance to employees for their day-to-day work. | Supervises, monitors performance, and provides feedback. |
| Long-term Perspective | Focuses on long-term vision and sustainable growth. | Focuses on maintaining effective administrative systems. | Balances short-term and long-term objectives to achieve goals. |
| Examples | CEO, Team Leader, Visionary. | HR Manager, Office Administrator. | Project Manager, Operations Manager, Department Head. |
How Ethical Processes are useful in establishing Brand?
-
Building Trust: Ethical processes build trust by demonstrating honesty, integrity, and transparency, which is vital for establishing a strong brand reputation.
-
Enhancing Brand Image: Ethical processes showcase a brand's values, making it known as a responsible and trustworthy entity, setting it apart from competitors.
-
Meeting Customer Expectations: Ethical processes ensure that a brand's products or services meet high-quality standards, safety regulations, and ethical sourcing practices, satisfying customer expectations.
-
Attracting and Retaining Talent: Brands known for ethical practices attract top talent, as employees are motivated and engaged when working for an organization that upholds ethical values.
-
Mitigating Risks and Crises: Ethical processes help identify and address potential risks and crises proactively, minimizing legal, reputational, and financial risks to safeguard the brand's reputation.
-
Gaining Competitive Advantage: Ethical processes differentiate a brand from competitors, appealing to customers who prioritize ethical considerations in their purchasing decisions.
-
Engaging Stakeholders: Ethical processes foster strong relationships with stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, and communities, leading to loyalty, support, and positive word-of-mouth.
-
Contributing to Society: Brands with ethical practices have the opportunity to make a positive impact by incorporating sustainability, supporting social causes, and engaging in ethical philanthropy, enhancing their brand value and attracting socially conscious consumers.
Explain various tools of Monetary Policy.
what are Quantitative tools and Qualitative tools of Monetary Policy
Quantitative Tools and Qualitative Tools are two categories of instruments used by central banks to implement monetary policy.
Quantitative Tools (General Credit Control Tools):
- Repo Rate: The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank provides liquidity to banks.
- Reverse Repo Rate: The interest rate at which the Reserve Bank absorbs liquidity from banks.
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF): Allows banks to borrow additional money from the Reserve Bank.
- Bank Rate (BR): The rate at which the Reserve Bank buys or rediscounts bills of exchange or commercial papers.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The percentage of a bank's net demand and time liabilities it must keep with the Reserve Bank.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): The percentage of a bank's net demand and time liabilities it must maintain in safe and liquid assets.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs): The purchase and sale of government securities to inject or absorb liquidity.
- Market Stabilization Scheme (MSS): Absorbs excess liquidity through the sale of short-dated government securities.
Qualitative Tools (Selective Credit Control Tools):
- Credit Rationing: Lenders limit the supply of credit, even if borrowers are willing to pay higher interest rates.
- Margin Requirements: The percentage of marginable securities a customer must pay for a loan or credit.
Define: 1. Cash Reserve Ratio, 2. Statutory Liquidity ratio, 3. Repo rate 4. Reverse repo rate.
-
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): CRR is the percentage of deposits that banks are required to keep as reserves with the central bank.
-
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): SLR is the percentage of deposits that banks are required to invest in safe and liquid assets such as government securities.
-
Repo Rate: Repo rate is the interest rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks against government securities.
-
Reverse Repo Rate: Reverse repo rate is the interest rate at which the central bank borrows money from commercial banks against government securities.
Enlist determinants of Demand and Supply.
Determinants of Demand:
- Price: Demand is inversely related to price; as price decreases, demand increases, and vice versa.
- Income: Higher income leads to increased demand, while lower income leads to decreased demand.
- Demography (Population): With an increase in population, demand tends to increase.
- Consumer Preferences: Demand is influenced by consumers' tastes and preferences. If they like a product, they demand more of it.
- Expectations of Future Price: If consumers anticipate a future price increase, they tend to demand more of the product in the present.
- Prices of Related Commodities: The demand for a product can be influenced by the prices of substitute products.
Determinants of Supply:
- Price: As the price of a product increases, suppliers are motivated to supply more to maximize profits, and vice versa.
- Supplier Strategies: Suppliers' decisions and strategies determine the quantity of goods they release at different prices.
- Number of Suppliers: The market structure, such as monopoly or competition, is determined by the number of suppliers, which affects the volume of supply.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as taxation, price controls, and incentives, can impact the supply of goods.
- Technology Development and Adoption: Technological advancements enable large-scale production at lower costs, influencing both consumers and suppliers.
- Future Expectations: Suppliers' expectations about future price changes can lead them to restrict or increase the supply accordingly.
- Natural Calamities: Natural disasters like floods, droughts, cyclones, earthquakes, etc., can disrupt the supply of goods.
Discuss the types of cost. Explain any two with examples.
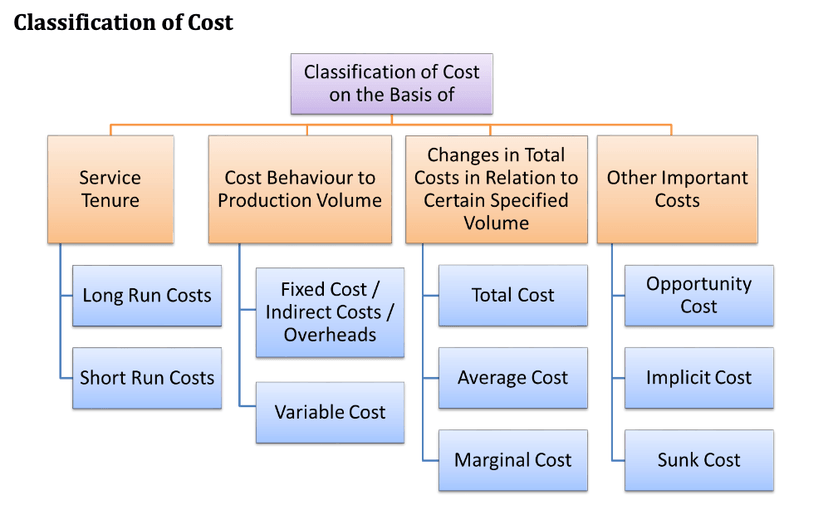
NOTE: Explain any two, So read any two
Classification of Cost on the Basis of Service Tenure:
- Long Run Costs: Costs incurred by firms when they change production levels over time, considering expected economic profits or losses. In the long run, all factors of production can vary.
- Short Run Costs: Costs accumulated in real-time during the production process. Only variable costs and revenues affect short-run production. Short-run costs depend on the rate of production and variable costs.
Comparison between Short Run and Long Run Cost:
- Long Run Costs: No fixed factors of production; market variables fully adjust to the state of the economy.
- Short Run Costs: Both fixed and variable factors of production exist; market variables do not always adjust due to the condensed time period.
Classification of Cost on the Basis of Cost Behavior to Production Volume:
- Fixed Costs (Indirect Costs/Overheads): Business expenses that do not depend on the level of goods or services produced, such as salaries or rents paid per month.
- Variable Costs: Costs that change in proportion to the quantity of goods or services produced, such as the cost of direct materials and direct labor.
Classification of Cost on the Basis of Changes in Total Costs in Relation to Certain Specified Volume:
- Total Cost: The sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost.
- Average Cost: The average cost per unit obtained by dividing the total cost by the volume of production.
- Marginal Cost: The additional cost incurred when producing one more unit of a product.
Some Other Important Costs:
- Opportunity Cost: The cost incurred by choosing one alternative over another, resulting in the loss of potential benefits from the unchosen alternative.
- Implicit Cost: The opportunity cost associated with an investment or decision, calculated based on the forgone benefits.
- Sunk Cost: Costs incurred that cannot be recovered, such as government fees, registration fees, or consultancy fees, even if the associated business or project is not pursued.
Explain the importance of the subject Principles of Economics and Management as part of B. E. study.
NOTE: it's for 7 marks by length, so read accordingly
-
Foundation of Business Knowledge: Principles of Economics and Management provides a solid foundation for understanding the fundamental concepts and principles that drive business operations and decision-making.
-
Understanding Economic Principles: The subject helps students grasp key economic principles such as supply and demand, market structures, pricing mechanisms, and resource allocation. This knowledge is crucial for making informed business decisions.
-
Insight into Business Environment: Principles of Economics and Management enables students to understand the broader economic environment in which businesses operate. This includes factors such as inflation, unemployment, fiscal policies, and international trade.
-
Decision-Making Skills: Studying economics and management equips students with analytical and critical thinking skills necessary for effective decision-making. They learn to evaluate costs and benefits, assess risks, and make informed choices to achieve business objectives.
-
Strategic Planning and Resource Allocation: The subject provides insights into strategic planning, including market analysis, competitor assessment, and resource allocation. Students learn how to develop business strategies that align with economic conditions and maximize efficiency.
-
Entrepreneurship and Innovation: Principles of Economics and Management nurtures an entrepreneurial mindset by fostering an understanding of market dynamics, customer needs, and innovation. It encourages students to identify business opportunities and develop innovative solutions.
-
Ethical Business Practices: The subject emphasizes the importance of ethical behavior and social responsibility in business operations. Students learn about ethical frameworks, corporate social responsibility, and the impact of business decisions on society and the environment.
-
Collaboration and Leadership Skills: Economics and management education promotes teamwork, communication, and leadership skills. Students learn to collaborate effectively, delegate tasks, and inspire teams to achieve common goals.
-
Adaptability to Changing Business Environment: Principles of Economics and Management equips students with knowledge and skills to navigate dynamic and evolving business environments. They learn to anticipate market changes, respond to challenges, and adapt their strategies accordingly.
-
Career Opportunities: A strong foundation in economics and management opens up diverse career opportunities in various sectors such as finance, consulting, marketing, operations, entrepreneurship, and more. It provides a broad skill set applicable across industries.
Explain the exception to the law of demand.
Exceptions to the Law of Demand:
- Veblen Goods:
- Veblen goods are luxury goods that defy the law of demand.
- As the price of these goods increases, their demand also increases.
- This is because the higher price enhances their perceived status and exclusivity, making them more desirable.
- Giffen Goods:
- Giffen goods are inferior goods that exhibit an upward-sloping demand curve.
- When the price of a Giffen good increases, consumers who are already struggling to afford basic necessities may be forced to allocate more of their limited income to the Giffen good.
- As a result, they buy even more of the Giffen good, leading to an increase in demand.
- Speculative Goods:
- Speculative goods are goods whose demand is driven by expectations of future price changes.
- If consumers anticipate that the price of a good will increase in the future, they may buy more of it even when the price is already high, defying the law of demand.
- Necessities during Emergency:
- In times of emergencies or crises, the demand for certain necessities like food, water, and medical supplies may increase regardless of their price.
- The urgent need for these goods overrides the typical price-demand relationship.
- Superior Goods:
- Superior goods are goods for which demand increases as consumer income increases.
- These goods are associated with higher quality and are often seen as a status symbol.
- As consumers' income rises, their demand for superior goods increases, even if their prices remain the same or slightly higher.
NOTE: It is important to note that these exceptions to the law of demand are relatively rare and may not apply to all goods and situations. The law of demand generally holds true, stating that as the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
How do you define culture? How does culture affect management style?
Definition of Culture:
- Culture refers to the shared beliefs, values, customs, behaviors, and artifacts that characterize a particular group or society.
- It encompasses the way people think, behave, communicate, and interact within a specific social group or organization.
Impact of Culture on Management Style:
-
Culture significantly influences management style and practices within an organization.
-
Management style is shaped by cultural norms, values, and expectations prevalent in a particular society or group.
-
Cultural factors influence decision-making processes, communication styles, leadership approaches, and employee interactions.
-
In hierarchical cultures, management tends to be more authoritative and centralized, with a clear chain of command and strict adherence to rules.
-
In more egalitarian cultures, management style may be more participative, collaborative, and focused on consensus-building.
-
Culture also affects attitudes towards risk-taking, innovation, and the balance between individual and collective goals.
-
Cultural diversity within an organization may require managers to be flexible and adaptive in accommodating different cultural perspectives and practices.
-
Effective managers understand the cultural context in which they operate and adapt their management style accordingly to foster a positive work environment and achieve organizational goals.
-
culture encompasses shared beliefs and behaviors within a group, and it significantly influences management style by shaping decision-making, communication, leadership approaches, and employee interactions. Understanding and respecting cultural differences is essential for effective management and fostering a harmonious work environment.
What are the types of Organizational Cultures? Explain in brief.
Types of Organizational Cultures:
- Clan Culture:
- Emphasizes collaboration, teamwork, and a family-like atmosphere.
- Values loyalty, employee development, and long-term relationships.
- Leaders act as mentors or facilitators, fostering a supportive work environment.
- Adhocracy Culture:
- Emphasizes innovation, creativity, and risk-taking.
- Values flexibility, experimentation, and adaptability.
- Leaders encourage entrepreneurship and empower employees to take initiative.
- Market Culture:
- Emphasizes competition, goal achievement, and results.
- Values performance, efficiency, and profitability.
- Leaders are focused on setting clear objectives and driving outcomes.
- Hierarchy Culture:
- Emphasizes stability, control, and formal procedures.
- Values rules, policies, and clear roles and responsibilities.
- Leaders maintain authority and ensure compliance with established processes.
Explain Monopolistic Market with its characteristics.
- In the real world, perfect competition and monopoly are extreme market structures that are not commonly found.
- Monopolistic competition is a more realistic market structure for modern businesses.
- In monopolistic competition, there are many firms producing similar goods, but with slight differences.
- These differences create a sense of uniqueness for each product, allowing firms to charge higher prices compared to their production costs.
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition Market:
- Large number of buyers:
- There is a significant number of buyers who demand specific products with close substitutes.
- Buyers have the flexibility to switch to alternative substitutes if there are unfavorable changes in the market.
- Large number of suppliers:
- While monopolistic competition has more suppliers compared to a monopoly, it has fewer suppliers than perfect competition.
- Multiple firms compete in the market, offering similar but differentiated products.
- Product differentiation:
- In monopolistic competition, products are differentiated from each other through branding, quality variations, packaging, or other marketing tactics.
- This product differentiation creates a perception of uniqueness and allows firms to target specific market segments.
- Less entry and exit barriers:
- There are relatively fewer barriers for new firms to enter the market and existing firms to exit.
- This ease of entry and exit promotes competition and allows new players to enter the market relatively easily.
- Advertisement expenditure:
- In monopolistic competition, firms often need to allocate a significant budget for advertising and promotional activities.
- Effective advertising helps create brand awareness and differentiate products from competitors.
- Price sensitivity:
- Consumers in monopolistic competition are highly price-sensitive.
- Even a slight change in price can influence their purchasing decisions, and they may switch to alternative products if the price is not favorable.
- The concept of group or chain:
- In monopolistic competition, there is a tendency for firms to form groups, chains, or franchises.
- These alliances or associations provide a mild form of unification and can offer advantages in terms of economies of scale, marketing power, and increased market presence.
Explain the types of managers with examples.
Types of Managers in an Organization:
- Top-Level Management:
- Ultimate source of authority and decision-making.
- Focus on planning and coordinating functions.
- Control and coordinate activities of the entire organization.
- Prepare goals, strategic plans, and policies.
- Provide direction and maintain external contacts.
- Examples: Board of directors, CEO, managing director.
- Middle-Level Management:
- Implement policies and strategies formulated by top-level management.
- Make plans for sub-units or departments.
- Interpret and communicate top-level policies to lower-level employees.
- Send important reports and data to top-level management.
- Inspire and motivate lower-level managers.
- Examples: Branch managers, departmental managers.
- Lower-Level Management:
- Also known as supervisory or operative level management.
- Responsible for quality and quantity of production.
- Act as a communication link between higher-level management and workers.
- Communicate workers' problems and suggestions to higher-level management.
- Help solve worker grievances and provide training.
- Arrange necessary materials, machines, and tools.
- Prepare periodic reports on worker performance.
- Ensure discipline and motivate workers.
- Examples: Supervisors, foremen, section officers, superintendents.
Ethical Behavior is doing what is morally right. Justify it.
- Ethical behavior refers to actions that align with moral principles and doing what is considered morally right.
justifications for ethical behavior:
-
Promotes Trust: Ethical behavior builds trust and credibility among individuals and within organizations, fostering positive relationships and cooperation.
-
Upholds Integrity: Acting ethically demonstrates integrity by adhering to ethical standards and principles, even in challenging situations.
-
Ensures Fairness: Ethical behavior promotes fairness and equality by treating others with respect and providing equal opportunities.
-
Enhances Reputation: Ethical conduct enhances an individual's or organization's reputation, leading to positive perceptions from others.
-
Encourages Accountability: Ethical behavior holds individuals accountable for their actions and decisions, promoting responsibility and transparency.
-
Promotes Long-Term Success: By following ethical practices, individuals and organizations establish a foundation for sustainable success and growth.
-
Supports Social Responsibility: Ethical behavior considers the impact of actions on society, promoting responsible and mindful decision-making.
-
Builds Positive Culture: Ethical behavior contributes to the development of a positive organizational culture, fostering employee satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
-
Mitigates Risks: Acting ethically reduces the risk of legal and regulatory issues, reputational damage, and negative consequences.
-
Reflects Personal Values: Engaging in ethical behavior aligns actions with personal values, contributing to personal fulfillment and a sense of purpose.
What is the difference between line and staff organization structures?
| Aspect | Line Structure | Staff Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Top-down authority. | Provides expertise but lacks direct authority. |
| Responsibility | Core operational activities and goal achievement. | Specialized support for goal attainment. |
| Operational Involvement | Hands-on involvement in daily operations. | Indirect involvement, providing advice and support. |
| Reporting Relationship | Direct reporting relationship. | Indirect reporting relationship. |
| Accountability | Accountable for outcomes. | Accountable for support and guidance. |
| Suitability | Smaller organizations with simple hierarchies. | Larger organizations with complex operations. |
| Decision-Making Power | Line managers make decisions. | Staff provides advice, no direct decision-making. |
| Authority Type | Line authority. | Functional authority. |
List the function of RBI in governing the banking system in India.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governs the banking system in India through various functions:
- Currency Issuance:
- RBI has the sole right to issue currency notes, except one-rupee notes.
- Banker to Government:
- RBI acts as the banker, agent, and advisor to the government, managing its finances.
- Banker's Bank:
- RBI manages and supervises scheduled banks, ensuring liquidity management and acting as a clearing house.
- Controller of Credit:
- RBI administers control over credit granted by commercial banks, regulating money supply.
- Custodian of Foreign Exchange Reserve:
- RBI maintains foreign exchange reserves and regulates exchange transactions.
- Data Collection and Publicity:
- RBI collects and publishes statistical data on various economic aspects.
- Promotional Functions:
- RBI promotes banking habits, expands the banking network, and supports finance for foreign trade.
- Supervisory Functions:
- RBI grants banking licenses, inspects banks, regulates non-banking financial institutions, and implements deposit insurance schemes.
These functions enable the RBI to effectively govern the banking system, maintain stability, and promote economic development in India.
Write a short note on hybrid organization.
- Hybrid organizations combine for-profit and nonprofit elements to tackle social or environmental issues and earn revenue.
- Their mission is twofold: achieving social impact and financial sustainability.
- By using business strategies and diverse funding sources, hybrids drive positive change, attract talent, and address gaps in other sectors.
- The integration of profit-driven activities with social responsibility allows hybrids to make a significant impact on society.
- Overall, hybrid organizations offer an innovative and impactful approach to address societal challenges while ensuring financial viability.
A hybrid organizational structure combines different approaches to design a company's internal operations. It integrates the best elements from various models while minimizing drawbacks.
Advantages:
- Alignment of corporate and divisional goals.
- Functional expertise and efficiency.
- Adaptability and flexibility in divisions.
Disadvantages:
- Conflicts between corporate departments and units.
- Excessive administration overhead.
- Slow response to exceptional situations.
A hybrid structure allows organizations to align goals, benefit from expertise and efficiency, and remain adaptable. However, conflicts, administrative burdens, and slower response times can pose challenges.
Many organizations do not have business ethics give your comments for the same.
The lack of business ethics within organizations can have serious negative consequences, both for the organization itself and for society as a whole. Here are a few comments on this issue:
- Reputation and Trust:
- Unethical behavior damages an organization's reputation and erodes trust with customers, employees, and stakeholders.
- Legal and Financial Risks:
- Unethical practices can lead to legal trouble, financial penalties, and instability for organizations.
- Employee Retention and Morale:
- Lack of ethics creates a toxic work environment, leading to high turnover rates and low morale among employees.
- Customer Dissatisfaction:
- Unethical practices, such as deceptive marketing or poor product quality, result in dissatisfied customers and loss of business.
- Social and Environmental Impact:
- Unethical organizations harm the environment, exploit workers, and contribute to social injustices, which invites public backlash.
- Long-Term Sustainability:
- Prioritizing short-term gains over ethics hinders long-term success, as sustainable growth requires trust and alignment with societal values.
To thrive and positively impact society, organizations must prioritize business ethics, promote transparency, and foster a culture of integrity.
Seven marks
Write a note on ‘Equilibrium between supply and demand’ with neat diagram
Write a detailed note on ‘Demand and supply Equilibrium’ with diagram.(winter-4)
- Equilibrium between supply and demand occurs when the quantity supplied by producers matches the quantity demanded by consumers. - Graphically, equilibrium is represented by the point where the supply curve and the demand curve intersect. - The supply curve slopes upward, indicating that as the price increases, producers are willing to supply more of the product. - The demand curve slopes downward, indicating that as the price increases, consumers are willing to buy less of the product. - The equilibrium point is the market equilibrium, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and there is no excess supply or demand. - The equilibrium price, or market-clearing price, is determined by the forces of supply and demand. - Prices above the equilibrium price result in excess supply, while prices below the equilibrium price result in excess demand. - Understanding equilibrium between supply and demand is crucial in analyzing how changes in factors such as costs, preferences, or policies can impact prices and quantities in a market.
How the prices of goods are determined by market? Discuss significance of demand and supply of goods in price determination.
Price Determination:
- The intersection of the demand and supply curves determines the equilibrium price in a market.
- At this equilibrium point, the quantity demanded matches the quantity supplied, and there is no excess supply or demand.
- If the price is below the equilibrium level, there will be excess demand, leading to upward pressure on prices.
- Conversely, if the price is above the equilibrium level, there will be excess supply, putting downward pressure on prices.
- Through the process of market competition, prices adjust until the equilibrium is reached, balancing supply and demand.
Significance of Demand and Supply in Price Determination:
- Demand and supply play a crucial role in price determination as they reflect consumer preferences and producer behavior.
- Changes in demand or supply can lead to shifts in the equilibrium, resulting in price adjustments.
- Increases in demand or decreases in supply generally lead to higher prices, while decreases in demand or increases in supply tend to lower prices.
- Understanding the dynamics of demand and supply helps businesses make pricing decisions and allows policymakers to assess market conditions.
- Market forces of demand and supply ensure that prices adjust to reflect the underlying economic realities of scarcity, preferences, and resource availability.
GDP, GNP, NNP and NDP. Explain these concepts in detail.
Write the full forms of GDP, GNP, NNP and NDP. Explain these concepts and elaborate how they are calculated
- GDP: Gross Domestic Product
- GDP is the total value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specific period (usually a year).
- It measures the economic activity within the geographical boundaries of a country, regardless of the nationality of the producers.
- GDP includes the value of goods and services produced by individuals, businesses, and the government.
- It is calculated using the expenditure approach (summing up consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports) or the income approach (summing up wages, profits, rents, and taxes).
- GNP: Gross National Product
- GNP is the total value of all final goods and services produced by the residents of a country, both domestically and abroad, during a specific period.
- It measures the economic output of a country's citizens, regardless of where the production takes place.
- GNP includes the value of goods and services produced domestically by residents as well as the income earned by residents from abroad.
- It is calculated by adding net income from abroad (income earned by residents from foreign sources) to GDP.
- NNP: Net National Product
- NNP is the value of the final goods and services produced by the residents of a country after accounting for depreciation (wear and tear on capital goods).
- It takes into account the amount of capital that is consumed or depreciated in the production process.
- NNP is calculated by subtracting depreciation (capital consumption) from GNP.
- NDP: Net Domestic Product
- NDP is the value of the final goods and services produced within a country's borders after accounting for depreciation.
- It measures the net output or income generated by the country's domestic economic activity.
- NDP is calculated by subtracting depreciation from GDP.
Calculation Example: Let's consider an example to illustrate these concepts:
- Assume a country has a GDP of 100 billion, and depreciation is $200 billion.
- The GNP would be 100 billion = $1,100 billion.
- The NNP would be 200 billion = $900 billion.
- The NDP would be 200 billion = $800 billion.
Explain importance on national income. And define following term GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP.
Importance of National Income:
- Economic Performance:
- National income serves as a key indicator of a country's economic performance. It helps measure the overall production and income generated within the economy, reflecting its economic growth and productivity.
- Standard of Living:
- National income is closely related to the standard of living of the population. Higher national income indicates greater potential for individuals to have higher incomes, access to better quality goods and services, and improved living conditions.
- Policy Formulation:
- National income data plays a crucial role in policy formulation by governments and central banks. It helps in assessing the impact of economic policies, formulating fiscal and monetary policies, and addressing issues related to employment, inflation, and poverty.
- International Comparisons:
- National income allows for comparisons of the economic performance and living standards between different countries. It provides insights into the relative economic positions, competitiveness, and development levels of nations.
- Investment and Business Decisions:
- National income figures are important for investors, businesses, and multinational corporations. They help in evaluating market potential, identifying growth opportunities, and making investment decisions based on the economic performance of a country.
Definitions of GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP:
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product):
- GDP is the total value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specific period, typically a year. It measures the economic activity within the geographical boundaries of a country.
- GNP (Gross National Product):
- GNP is the total value of all final goods and services produced by the residents of a country, both domestically and abroad, during a specific period. It includes the income earned by residents from abroad.
- NDP (Net Domestic Product):
- NDP is the value of the final goods and services produced within a country's borders after deducting depreciation. It takes into account the wear and tear on capital goods during the production process.
- NNP (Net National Product):
- NNP is the value of the final goods and services produced by the residents of a country after accounting for depreciation. It measures the net output or income generated by the country's residents, considering the depreciation of capital goods.
Write a detailed note on: 1.Monopoly Market 2.Oligopoly Market
- Monopoly Market:
-
Monopoly refers to a market structure where a single firm dominates the entire market and has exclusive control over the production and supply of a particular product or service. Here are the key features and characteristics of a monopoly market:
-
Single Seller: In a monopoly, there is only one seller or producer of the product or service, which gives them significant market power and control.
-
Unique Product: The monopolist offers a unique product that has no close substitutes in the market. Consumers have no alternative options to choose from.
-
Barriers to Entry: Monopolies typically have high barriers to entry, which make it difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete. These barriers can be legal, technological, or financial in nature.
-
Price Maker: The monopolist has the power to set the price of the product or service based on its own discretion. It can choose to charge higher prices due to the lack of competition.
-
Control over Supply: The monopolist has control over the supply of the product, allowing them to manipulate the quantity produced and adjust it according to market conditions.
-
Limited Consumer Choice: With no or limited competition, consumers have fewer choices and are often at the mercy of the monopolist's pricing and quality decisions.
-
Potential for Higher Profits: Monopolies can earn substantial profits due to their market dominance and ability to set prices above production costs.
-
- Oligopoly Market:
-
Oligopoly is a market structure characterized by a small number of large firms that dominate the market. In an oligopoly, these firms have significant market share and influence over pricing and market behavior. Here are the key features and characteristics of an oligopoly market:
-
Few Large Firms: In an oligopoly, there are only a few dominant firms that control a significant portion of the market. Each firm's actions and decisions can impact the overall market dynamics.
-
Interdependence: Oligopolistic firms are interdependent, meaning that the actions and strategies of one firm directly affect the others. They closely monitor and react to their competitors' moves.
-
Product Differentiation: Oligopolies often engage in product differentiation to make their products appear unique or superior to gain a competitive edge. This can be achieved through branding, marketing, or innovation.
-
Barriers to Entry: Oligopolistic markets have high barriers to entry, making it challenging for new firms to enter and establish themselves. This strengthens the market position of existing firms.
-
Non-Price Competition: Oligopolies tend to compete through non-price factors such as advertising, product quality, customer service, and innovation rather than solely on price.
-
Price Rigidity: Oligopolistic firms are reluctant to change prices frequently due to the fear of triggering price wars or aggressive reactions from competitors. Prices often remain relatively stable.
-
Collusion and Cartels: In some cases, oligopolistic firms may collude to control prices and limit competition. They may form cartels to regulate output and fix prices, which can be illegal in many jurisdictions.
-
Game Theory: Oligopolies are often analyzed using game theory to understand the strategic interactions and decision-making of firms in the market.
-
Compare and Contrast Monopoly and Perfect Competition markets. (4 marks)
What is monopoly? Differentiate between perfect competition and monopolistic competition
Monopoly
- Monopoly refers to a market structure where a single firm has exclusive control over the production, distribution, and sale of a particular product or service, giving them significant market power. In a monopoly, there are no close substitutes for the product or service offered, and the monopolistic firm becomes the sole provider, allowing it to dictate prices and quantities.
Here's a comparison between perfect competition and monopolistic competition:
| Perfect Competition | Monopolistic Competition | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Firms | Many firms | Many firms |
| Product Differentiation | Homogeneous products | Differentiated products |
| Entry Barriers | Low or no barriers | Low barriers |
| Pricing Power | Price takers | Some control over pricing |
| Nature of Demand Curve | Perfectly elastic | Downward sloping |
| Competition Level | Intense competition | Moderate competition |
| Branding and Advertising | Minimal or none | Extensive branding and advertising |
| Examples | Agricultural markets, stock exchanges, foreign exchange markets | Restaurants, clothing stores, personal care products, local specialty shops |
Define Financial Management. Discuss Function Of Financial Management.
Financial Management:
- Financial management involves planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring an organization's financial resources to maximize value and ensure financial health.
Functions of Financial Management:
- Financial Planning:
- Developing a comprehensive financial plan, setting budgets, and forecasting future financial needs.
- Capital Budgeting:
- Evaluating investment opportunities and making decisions on allocating funds to projects based on profitability and return on investment.
- Financing Decisions:
- Determining the optimal mix of financing sources (debt and equity) to fund operations and investments.
- Risk Management:
- Identifying and managing financial risks through strategies such as risk assessment, diversification, and hedging.
- Financial Control:
- Establishing internal controls, accounting systems, and financial reporting processes to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Financial Analysis and Reporting:
- Analyzing financial data, preparing financial statements, and generating reports to assess performance and guide decision-making.
- Cash Flow Management:
- Managing cash inflows and outflows, optimizing working capital, and ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet short-term obligations.
- Dividend Policy:
- Making decisions on distributing profits to shareholders through dividends based on factors such as profitability, cash flow, and growth opportunities.
Explain ‘Span of Control’. State merits and demerits of a limited span of control. Discuss the factors affecting the span of control.
Span of Control:
- Span of Control refers to the number of subordinates or employees that a manager can effectively supervise and manage.
- It determines the hierarchical structure and the number of levels in an organization.
- Narrow span of control
- Wide span of control
Factors Affecting the Span of Control:
- Complexity of Tasks:
- Complex tasks may require more direct supervision, leading to a narrower span of control.
- Employee Competence:
- The competence and experience of employees can influence the span of control, as more skilled and independent employees may require less supervision.
- Nature of Work:
- The type of work being performed, such as routine tasks or specialized projects, can impact the span of control.
- Managerial Skills:
- The capabilities and managerial skills of the supervisors play a role in determining the appropriate span of control.
- Technology and Communication Systems:
- Advanced technology and efficient communication systems can enable managers to handle a larger span of control.
Merits of a Limited Span of Control:
- Close Supervision:
- Managers can provide personalized attention and guidance to subordinates.
- Better Communication:
- Shorter communication channels result in clearer and efficient communication.
- Control and Coordination:
- Effective control and coordination as managers can devote more time to each subordinate.
- Skill Development:
- Managers can focus on developing the skills of subordinates more effectively.
Demerits of a Limited Span of Control:
- Hierarchical Levels:
- Taller organizational structure with slower decision-making and increased bureaucracy.
- Increased Costs:
- Higher administrative costs and overhead expenses.
- Bottlenecks and Delays:
- Potential bottlenecks and delays in information flow and decision-making.
- Limited Autonomy:
- Subordinates may have limited decision-making authority.
Define following terms with respect to banking 1. Repo Rate 2. Reverse Repo Rate 3.Marginal Standing Facility 4.Cash Reserve Ratio 5. Statutory Liquidity Ratio 6.Market Stabilization Scheme
- Repo Rate:
- Rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks.
- Used as a tool to control inflation and liquidity in the economy.
- Influences borrowing costs for banks and impacts lending rates in the economy.
- Reverse Repo Rate:
- Rate at which the central bank borrows money from commercial banks.
- Used to absorb excess liquidity from the banking system.
- Encourages banks to lend to the central bank instead of lending to other entities or individuals.
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF):
- Window provided by the central bank for overnight borrowing by commercial banks.
- Used in emergency or temporary liquidity shortages.
- Interest rate charged under MSF is generally higher than the repo rate.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- Portion of a bank's deposits that it must keep as reserves with the central bank.
- Regulates liquidity in the banking system.
- Higher CRR reduces lending capacity of banks and lowers liquidity, while lower CRR increases liquidity.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR):
- Percentage of certain assets that banks must maintain as reserves.
- Ensures banks have a certain level of liquidity.
- Regulated by the central bank to control liquidity and influence lending capacity.
- Market Stabilization Scheme (MSS):
- Monetary policy tool to manage excess liquidity in the economy.
- Involves issuing securities by the central bank to absorb excess funds from banks.
- Helps in managing liquidity and stabilizing financial markets.
Explain CARROLL’S SOCIAL RESPONSILITY PYRAMID
Certainly! Here's a revised version with a bit more detail:
- Economic Responsibility:
- This is the foundation of the pyramid and refers to a business's fundamental responsibility to be profitable and contribute to the economy.
- Organizations must generate revenue, create jobs, and provide goods or services that meet customer needs.
- Legal Responsibility:
- Businesses have a duty to operate within the framework of laws and regulations.
- They must fulfill their legal obligations towards stakeholders, employees, customers, and society as a whole.
- This includes adhering to labor laws, consumer protection laws, environmental regulations, and other applicable laws.
- Ethical Responsibility:
- Organizations are expected to conduct themselves in an ethical manner, making decisions that are fair, just, and socially responsible.
- They should avoid actions that may harm stakeholders and should engage in honest business practices.
- Ethical responsibility involves demonstrating integrity, transparency, and accountability in all business activities.
- Philanthropic Responsibility:
- This represents the highest level of corporate social responsibility and involves voluntary actions and contributions made by organizations to support social causes.
- Businesses go beyond their economic, legal, and ethical obligations to make a positive impact on society.
- Philanthropic activities may include charitable donations, community development programs, environmental initiatives, and employee volunteerism.
What is Break-Even Analysis? Mr. ABC is the managerial accountant in charge of soft-drink Company XYZ. According to him, fixed costs of company XYZ consist of property taxes, a lease, and salaries of staff, which add up to Rs. 1,00,000. The variable cost associated with producing one soft- drink bottle is Rs. 2 per unit which is sold at a premium price of Rs. 12 per unit. Determine the Break-Even Quantity. What would be Break Even Quantity if production cost becomes Rs. 4 per bottle?
Break-Even Analysis is a financial and managerial accounting tool used to determine the point at which a company's total revenue equals its total cost, resulting in zero profit or loss. In other words, it helps to find the quantity of goods or services a company needs to sell to cover its total costs and start making a profit.
To calculate the Break-Even Quantity (BEQ), we use this formula:
Break-Even Quantity = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit)
Let's use an example for a soft-drink company called XYZ:
Fixed Costs (the costs that don't change) = Rs. 1,00,000 Variable Cost per Bottle (cost that changes per bottle) = Rs. 2 Selling Price per Bottle (the price at which they sell) = Rs. 12
Now, we plug these values into the formula:
Break-Even Quantity = Rs. 1,00,000 / (Rs. 12 - Rs. 2) Break-Even Quantity = Rs. 1,00,000 / Rs. 10 Break-Even Quantity = 10,000 bottles
So, the Break-Even Quantity for Company XYZ is 10,000 bottles. It means they need to sell 10,000 bottles to cover all their costs.
Now, let's say the production cost becomes Rs. 4 per bottle:
Fixed Costs = Rs. 1,00,000 Variable Cost per Bottle = Rs. 4 Selling Price per Bottle = Rs. 12
We use the formula again:
Break-Even Quantity = Rs. 1,00,000 / (Rs. 12 - Rs. 4) Break-Even Quantity = Rs. 1,00,000 / Rs. 8 Break-Even Quantity = 12,500 bottles
So, if the production cost becomes Rs. 4 per bottle, the new Break-Even Quantity for Company XYZ would be 12,500 bottles. They would need to sell 12,500 bottles to cover all their costs.
List and Explain various type costs in production with suitable example.
- Fixed Costs:
- Costs that don't change, regardless of how much you produce.
- Example: Rent for a factory. It stays the same whether you make 100 or 1000 units.
- Variable Costs:
- Costs that vary based on how much you produce.
- Example: The cost of raw materials. If you make more products, you need more materials.
- Total Cost:
- Total cost is the sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost.
- 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡(𝑇𝐶)=𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐹𝑖𝑥𝑒𝑑 𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡(𝑇𝐹𝐶)+𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑉𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 (𝑇𝑉𝐶).
- Marginal Costs:
- The cost to produce one additional unit.
- Example: If making 100 shirts costs Rs. 5000 and making 101 shirts costs Rs. 5050, the marginal cost is Rs. 50.
- Average Costs:
- Total costs divided by the number of units produced.
- Example: If you spend Rs. 1000 to make 50 products, the average cost is Rs. 20 per product.
- Opportunity Costs:
- The value of the next best option you give up when making a choice.
- Example: A farmer has a piece of land, and growing wheat means they can't grow potatoes, so the opportunity cost is the potential potato yield.
- Sunk Costs:
- Costs that have already been spent and can't be recovered.
- Example: Spending money on a marketing campaign, and later deciding not to launch the product. The marketing expenses are sunk costs.
How the size of economy of a nation/region can be measured? Which are the various factors which can be helpful to attract foreign investments?
-
GDP: GDP is the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders in a year. It measures the size and performance of an economy.
-
GNP: GNP measures the total value of goods and services produced by a country's residents, including those produced abroad, in a specific period.
-
GNI: GNI is the total income earned by a country's residents, both domestically and internationally. It includes GDP and net income from abroad.
-
Per Capita Income: Per Capita Income is the average income per person in a country, calculated by dividing the total income (GNI or GDP) by the population. It reflects individual economic well-being.
-
PPP: PPP adjusts GDP or GNI to consider the purchasing power of different currencies, allowing for a better comparison of living standards between countries.
-
HDI: HDI measures a country's overall development and well-being by considering factors like life expectancy, education levels, and per capita income.
-
Unemployment Rate: This percentage indicates the proportion of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking employment. It reflects the job market situation.
Factors to Attract Foreign Investments:
-
Stable Political Environment: A stable and predictable political environment fosters investor confidence.
-
Business-Friendly Policies: Pro-investment policies, low tax rates, and streamlined regulations attract foreign investors.
-
Skilled Workforce: A well-educated and skilled labor force is attractive to businesses seeking talent.
-
Infrastructure: Good infrastructure, including transportation and communication networks, enhances business operations.
-
Natural Resources: Abundant natural resources can attract foreign investments in sectors like mining and energy.
-
Market Size: A large domestic market with high purchasing power can be appealing to investors.
-
Economic Growth Prospects: Positive economic growth projections indicate potential returns on investments.
-
Legal and Regulatory Environment: A strong legal system and protection of property rights provide a secure investment environment.
-
Trade Agreements: Being part of trade agreements or economic blocs can enhance market access for investors.
-
Political Stability: Political stability and a favorable investment climate reduce risks for foreign investors.
Unemployment, Poverty, Poor Education, and Poor Public Health Infrastructure, How these social problems are interlinked? Discuss with reasonable arguments.
-
Unemployment and Poverty:
- When people don't have jobs (unemployment), they struggle financially, leading to poverty.
- Being poor makes it difficult to access education and healthcare, making it harder to find jobs, creating a cycle.
-
Poverty and Poor Education:
- Being poor can limit access to good education due to money problems.
- Without proper education, it's challenging to get better jobs, which can keep people trapped in poverty.
-
Poor Education and Unemployment:
- Having a weak education can make it harder to find work.
- Limited job opportunities can lead to unemployment.
-
Poor Public Health Infrastructure and Poverty:
- A weak healthcare system can lead to high medical expenses, pushing people into poverty.
- Poor communities may lack resources for better healthcare, impacting their quality of life.
-
Poverty and Poor Public Health Infrastructure:
- Poverty-stricken areas often lack resources to invest in good healthcare.
- This can lead to worse health outcomes for people living in poverty.
-
Poor Public Health Infrastructure and Unemployment:
- Weak healthcare can lead to more health problems, reducing people's ability to work.
- This can result in higher unemployment rates in affected communities.
Addressing these issues requires working together to create job opportunities, improve education, and strengthen healthcare systems, ultimately breaking the cycle of poverty and improving the overall well-being of communities.
Compare and Contrast Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy.
Of course! Here's a simple and short comparison of Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy in tabular format:
| Aspect | Monetary Policy | Fiscal Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank regulates money supply and interest rates to control inflation and stabilize the economy. | Government uses spending, taxation, and borrowing to influence economic growth and stability. |
| Authority | Central bank (e.g., Federal Reserve) | Government (legislature and executive branches) |
| Objective | Control inflation and stabilize the economy. | Achieve full employment and stabilize economic growth. |
| Instruments | Interest rates, open market operations, reserve requirements, discount rate. | Government spending, taxation, government borrowing. |
| Impact on Economy | Affects money supply, credit availability, and interest rates. | Influences aggregate demand, disposable income, and economic activity. |
| Flexibility | More flexible, quick adjustments. | May require legislative approval, takes time to implement. |
| Responsiveness | Swift response to economic changes. | Longer lag time due to political process. |
| Focus | Financial markets and banking institutions. | Government revenue and spending. |
| Limitations | Limited effectiveness when interest rates are low. | Political constraints, potential deficits. |
| Coordination | Can be coordinated with fiscal policy for better results. | Coordination may be challenging due to separate authorities. |
“Management is combination of a Science and Art.” Justify the statement. 2
-
Science in Management:
- Systematic approach:
- Management follows a systematic approach based on scientific principles and methods.
- Scientific disciplines:
- Management draws upon psychology, economics, and sociology to understand human behavior and organizational dynamics.
- Data-driven decision making:
- Managers use data and analytics to make informed decisions.
- Systematic approach:
-
Art in Management:
- Creativity and innovation:
- Management requires creative thinking to develop new ideas and solutions.
- Leadership and communication:
- Effective management involves inspiring and motivating employees through strong leadership and communication skills.
- Adaptability and intuition:
- Managers rely on intuition and experience to navigate complex situations and make decisions.
- Creativity and innovation:
-
Synergy of Science and Art:
- Evidence-based decision making:
- The scientific aspect provides a foundation for objective analysis and decision making.
- Creative problem solving:
- The artistic aspect allows managers to think creatively and find innovative solutions.
- Holistic approach:
- By combining science and art, managers can take a comprehensive approach to management.
- Evidence-based decision making:
List and Explain Various Functions of Management.
- Planning:
- Setting goals, strategies, and action plans based on analysis and resource allocation decisions.
- Organizing:
- Structuring resources, tasks, and people through clear roles, structures, and communication channels.
- Staffing:
- Acquiring and developing talent through recruitment, training, and performance management.
- Directing:
- Guiding and supervising employees, providing instructions, resolving conflicts, and promoting teamwork.
- Coordinating:
- Harmonizing activities and resources across departments, teams, and processes for common goals.
- Controlling:
- Monitoring performance, setting standards, comparing actual results, and taking corrective actions.
- Decision Making:
- Analyzing information, evaluating options, and making informed choices aligned with objectives.
- Innovating:
- Encouraging creativity, embracing change, and seeking opportunities for improvement and growth.
Discuss the external and internal sources of recruitment in detail.
Discuss the internal and external sources of recruitment in detail.(winter 7)
Recruitment involves finding candidates for job vacancies, which can be done through external and internal sources. Let's discuss each source briefly:
- External Sources of Recruitment:
- Job Advertisements: Organizations advertise job vacancies through online portals, newspapers, and social media to reach a wide audience.
- Recruitment Agencies: Organizations partner with agencies that specialize in sourcing and screening candidates.
- Campus Placements: Organizations visit educational institutions to recruit fresh graduates.
- Employee Referrals: Employees refer suitable candidates from their networks.
- Professional Networking: Organizations connect with potential candidates through industry events and networking platforms.
- Internal Sources of Recruitment:
- Internal Job Postings: Organizations advertise job vacancies internally, allowing current employees to apply and advance their careers.
- Employee Promotions: High-performing employees are promoted to higher positions.
- Transfers: Employees are moved between departments or locations for new experiences and skill development.
- Talent Management Programs: Specialized programs identify and develop high-potential employees.
- Succession Planning: Potential candidates are prepared for key positions in the organization.
Explain the determinants of Elasticity of demand.
Explain elasticity of demand in detail.
Explain Elasticity of Demand in detail.(winter-4)
-
Elasticity of demand measures how responsive the quantity demanded of a product is to changes in different factors. It helps businesses understand how demand will change in various situations.
-
There are different types of demand elasticity:
-
Price Elasticity of Demand:
- It shows how demand changes when the price of a product changes.
- If demand is highly affected by price changes, it is called elastic. If not, it is inelastic.
- Factors like substitutes and necessity vs. luxury influence price elasticity.
- Price elasticity helps businesses predict how sales will be affected by price adjustments.
- It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price.
-
Income Elasticity of Demand:
- It measures how demand changes with shifts in consumer income.
- Normal goods have positive income elasticity, meaning demand increases as income rises.
- Luxury goods have higher income elasticity, while inferior goods have negative income elasticity.
- Income elasticity helps businesses understand how demand may shift with changes in consumer income.
- It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in income.
-
Cross Elasticity / Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand:
- It examines how the demand for one product changes when the price of another product changes.
- Substitute goods have positive cross elasticity, meaning demand increases when the price of a substitute rises.
- Complementary goods have negative cross elasticity, as demand for one increases when the price of the other falls.
- Cross elasticity helps businesses identify relationships between different products in the market.
- It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded of the first good by the percentage change in price of the second good.
-
Promotional Elasticity of Demand:
- It focuses on how promotional activities impact the quantity demanded.
- Promotional elasticity measures how demand changes in response to changes in sales volume and promotional expenses.
- Luxury products tend to have higher promotional elasticity compared to necessities.
- Promotional elasticity helps businesses assess the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Explain Law of variable proportion & law of return to scale.
- The Law of Variable Proportions and the Law of Returns to Scale are important principles in economics and management that help explain production processes and the relationship between inputs and outputs. Here is an explanation of these principles in the context of :
Law of Variable Proportions:
- Also known as the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns.
- It explains the relationship between inputs and outputs in the short run.
- When one input increases while others remain constant, the marginal product of that input eventually decreases.
- Managers use this law to understand how changes in input quantities affect production efficiency.
- In the short run, firms have fixed inputs (e.g., machinery) and variable inputs (e.g., labor).
- Initially, increasing the variable input leads to increased marginal product due to specialization and resource allocation.
- However, adding more of the variable input eventually results in diminishing marginal returns.
- Constraints from fixed inputs lead to reduced overall output per unit of the variable input.
- Understanding this law helps managers make informed decisions about input combinations and resource allocation.
Law of Returns to Scale:
- It explores the relationship between changes in production scale and resulting output changes.
- Managers use it to understand the impact of scaling production on productivity, costs, and efficiencies.
- In the long run, firms can adjust all inputs to expand or contract operations.
- Three possible outcomes when inputs increase or decrease proportionally:
- Increasing Returns to Scale: Output increases more than inputs, indicating economies of scale.
- Constant Returns to Scale: Output increases proportionally with inputs, maintaining efficiency.
- Decreasing Returns to Scale: Output increases less than inputs, indicating inefficiencies.
- Managers use this law to assess the implications of scaling operations and achieve cost advantages and efficiencies.
Discuss principles of Scientific Management. ### List out the principles of scientific
management.(winter-3)
- Frederick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915) is widely regarded as the "father of scientific management," which is a classical management approach focused on improving the efficiency of workers through the scientific study of work methods. Taylor introduced several key elements that form the principles of Scientific Management:
- Scientific Task Planning:
- Scientific task planning involves determining in advance the specific work to be done, who will do it, where and when it will be done.
- This helps ensure proper allocation of resources and effective scheduling of tasks.
- Time Study:
- Time study involves observing and recording the time taken by workers to complete specific tasks.
- This data is then used to establish standard times for completing those tasks, providing a benchmark for worker performance and enabling better planning and scheduling.
- Motion Study:
- Motion study aims to identify the most efficient sequence of steps or motions required to perform a particular task.
- By analyzing and eliminating unnecessary or wasteful movements, organizations can optimize work methods, reduce fatigue, and increase productivity.
- Functional Foremanship:
- Taylor introduced the concept of functional foremanship, where the factory is divided into various specialized departments, each headed by a specialist supervisor. This ensures that workers receive expert guidance and supervision in different aspects of their work, leading to increased efficiency and quality.
- Standardization:
- Standardization involves establishing predetermined standards for tasks, materials, work methods, quality, time, and working conditions. Standardization simplifies processes, reduces waste, improves quality, and maximizes resource utilization.
- Differential Piece Rate System:
- Taylor proposed a wage system based on the differential piece rate, which incentivizes workers based on their performance and competence. Competent workers are paid higher piece rates, encouraging them to maintain high productivity and quality. Incompetent workers are motivated to improve their skills to earn higher wages.
Explain the break even analysis with the help of suitable Curves and Assumptions. Also derive the formula for Break Even Quantity.
Explain break even analysis in detail.
Break-even analysis is a financial tool used to determine the point at which a company's total revenue equals its total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. It provides valuable insights into the minimum level of sales required to cover all expenses and is commonly used in business planning, pricing decisions, and determining the viability of a product or service. Let's dive into the details of break-even analysis: Certainly! Here's a version with smaller sentences, point-by-point format, and easy language:
Break-Even Analysis:
- Break-even analysis helps determine the point where a company's revenue equals costs, resulting in no profit or loss.
- It helps with business planning, pricing decisions, and assessing product or service viability.
Components of Break-Even Analysis:
- Fixed Costs: Costs that don't change with production or sales volume, like rent or salaries.
- Variable Costs: Costs that vary with production or sales volume, such as raw materials or direct labor.
- Total Costs: The sum of fixed and variable costs, representing all company expenses.
- Sales Revenue: Income generated from product or service sales.
Key Metrics in Break-Even Analysis:
- Break-Even Point (BEP):
- The sales level where total revenue equals total costs.
- It's calculated by dividing fixed costs by the contribution margin per unit or the contribution margin ratio.
- Contribution Margin:
- The difference between sales price per unit and variable cost per unit.
- It covers fixed costs and contributes to profit.
- Profit or Loss:
- Profit occurs when total revenue exceeds total costs, and loss occurs when costs exceed revenue.
- Margin of Safety:
- The difference between actual sales and the break-even point.
- Provides stability and flexibility.
Benefits and Applications of Break-Even Analysis:
- Pricing Decisions: Determines the minimum price to cover costs and achieve profitability.
- Business Planning: Forecasts sales volume, assesses project feasibility, and sets achievable sales targets.
- Cost Control: Identifies areas for cost reduction and control to improve profitability.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Assesses the impact of changing assumptions on the break-even point and profitability.
- Investment Evaluation: Evaluates financial viability and time required to recover the initial investment.
Limitations of Break-Even Analysis:
- Simplified Assumptions: Assumes linear relationships between costs, sales, and profits, which may not be accurate in reality.
- Ignoring External Factors: Doesn't consider market demand, competition, or changes in the business environment.
- Overemphasis on Volume: Focuses on sales volume and may overlook other factors impacting profitability.
- Limited Scope: More suitable for short-term decisions and may not fully analyze long-term business strategies. Despite these limitations, break-even analysis remains a valuable tool for businesses to assess profitability, make informed decisions, and understand the relationship between costs, sales, and profits. It provides a solid foundation for financial planning and helps identify critical factors that impact business success.
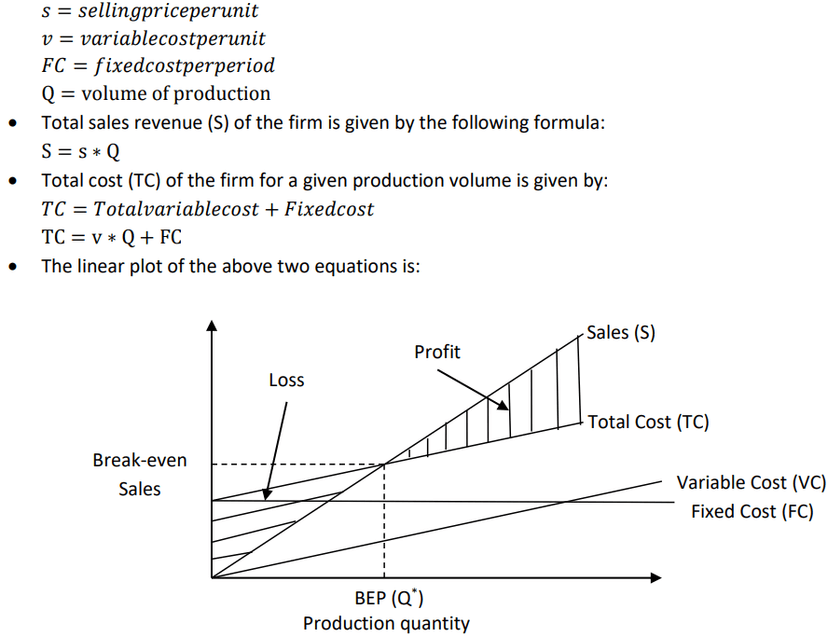
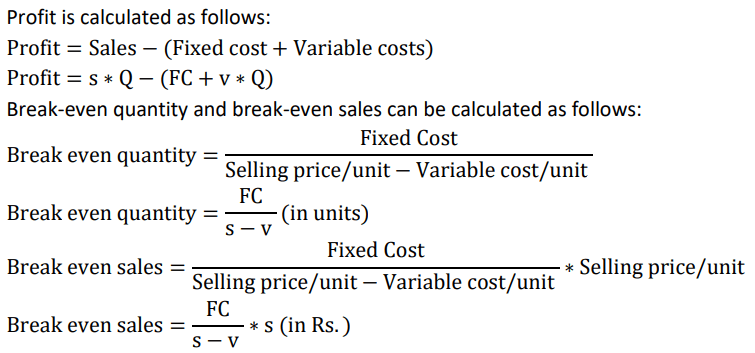
What are the basic economic problems? Explain in details and suggest some remedies to overcome these problems.
List out various economic problems.(winter-3)
- The basic economic problems, also known as the central economic problems, refer to the fundamental challenges faced by any economy. These problems arise due to the scarcity of resources relative to unlimited human wants and needs. The three main basic economic problems are:
- Poverty: Poverty refers to the condition of lacking sufficient income or resources to meet basic human needs. It is a complex social issue influenced by factors such as unequal distribution of wealth, lack of access to education and healthcare, limited job opportunities, and social exclusion. To address poverty, some remedies include:
- Economic growth
- Income redistribution
- Education and skills development
- Access to basic services
- Unemployment: Unemployment occurs when individuals are actively seeking work but are unable to find employment opportunities. It is a result of factors such as insufficient job creation, economic downturns, technological changes, and skills mismatch. Remedies for reducing unemployment include:
- Job creation
- Education and training
- Labor market policies
- Inflation: Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over time. It erodes the purchasing power of money and can disrupt economic stability. To mitigate inflation, some remedies include:
- Monetary policy
- Fiscal policy
- Supply-side policies
Remedies to Overcome Basic Economic Problems:
-
Economic Planning: Governments can play a crucial role in guiding resource allocation, making strategic decisions, and promoting sustainable development through effective economic planning.
-
Market Mechanisms: Market mechanisms, such as free markets and price systems, efficiently allocate resources based on supply and demand signals, helping determine what, how, and for whom to produce.
-
Technological Advancements: Embracing technological advancements and fostering innovation enhances productivity and efficiency. Investments in research, development, and the adoption of new technologies help overcome resource constraints and improve production methods.
-
Education and Skill Development: Quality education, vocational training, and lifelong learning programs equip individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to participate effectively in the economy, driving productivity and innovation.
-
Social Safety Nets: Establishing social safety nets, including welfare programs and unemployment benefits, addresses income inequality and safeguards vulnerable individuals and families during economic hardships, ensuring access to basic needs and promoting social cohesion.
-
International Trade: Engaging in international trade enables specialization, resource exchange, and access to a wider range of goods and services. Trade liberalization, removing barriers, and participating in global value chains contribute to economic growth, employment opportunities, and resilience.
Define CSR and discuss its due importance in industrial practice.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) means that businesses should operate in a way that considers society and the environment, not just their profits. It involves companies taking voluntary actions to deal with social, environmental, and ethical problems and make a positive difference in society.
The importance of CSR in industrial practice:
- Reputation and trust:
- CSR initiatives enhance a company's reputation and build trust among customers, employees, investors, and communities, differentiating it from competitors.
- Competitiveness:
- Embracing CSR attracts socially conscious customers, investors, and employees, providing a competitive advantage and contributing to long-term success.
- Risk management:
- CSR practices help identify and mitigate risks related to environmental, social, and governance factors, reducing the likelihood of legal, regulatory, and reputation-related challenges.
- Stakeholder engagement:
- CSR allows companies to engage with stakeholders and understand their expectations, fostering positive relationships with customers, employees, communities, suppliers, and regulators.
- Employee morale and productivity:
- CSR initiatives boost employee morale and engagement by aligning work with a broader purpose, attracting and retaining talented employees who share the company's values.
- Innovation and sustainability:
- CSR encourages companies to find innovative solutions to societal and environmental challenges, leading to long-term profitability and contributing to a more sustainable future.
- License to operate:
- Meeting societal expectations and fulfilling social responsibilities are vital for a company's continued operation, as governments, communities, and regulators increasingly demand responsible business practices.
Henri Fayol has stated 14 administrative principles of management. Enlist them and explain any four of them.
Henri Fayol, a French management theorist, proposed 14 administrative principles of management. They are as follows:
- Division of Work:
- Tasks and responsibilities should be divided among employees to increase efficiency and specialization.
- By dividing work, employees can focus on specific areas of expertise, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Stability and Tenure:
- Long-term employment and stability within the organization contribute to improved productivity and loyalty.
- Initiative:
- Employees should be encouraged to take initiative and show creativity in their work.
- By empowering employees to take ownership of their tasks, organizations can foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
- Unity of Command:
- Each employee should receive instructions and guidance from only one manager to avoid confusion and conflicts.
- It helps to avoid conflicts and confusion caused by receiving conflicting instructions from multiple managers. Clear lines of authority and reporting ensure a smoother flow of communication and decision-making.
- Unity of Direction:
- The organization should have a unified direction and shared objectives to align efforts and avoid conflicting goals.
- Subordination of Individual Interests:
- The interests of individuals should be subordinate to the interests of the organization as a whole.
- Remuneration:
- Employees should be fairly compensated for their work to ensure motivation and satisfaction.
- Centralization:
- The extent to which decision-making authority is concentrated at the top of the organization.
- Scalar Chain:
- A clear hierarchy of authority should exist within the organization, from top management to the lowest levels.
- It defines the chain of command and ensures that information and decisions flow through the proper channels.
- This principle helps in maintaining order, reducing conflicts, and facilitating effective communication.
- Order:
- Resources and personnel should be allocated in the most effective and efficient manner.
- Equity:
- Employees should be treated with fairness and justice to maintain a positive work environment.
- Authority and Responsibility:
- Managers should have the authority to give orders, and employees should have the responsibility to carry them out.
- Discipline:
- Employees should follow established rules and guidelines to maintain order and obedience within the organization.
- Esprit de Corps:
- Promoting teamwork, harmony, and a sense of unity among employees.
Explain Maslow’s theory of Hierarchy of Needs with necessary diagram.
Explain the theory of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
Explain Needs Maslow’s theory of management.(winter-4)
Maslow's theory of Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory proposed by Abraham Maslow that describes the different levels of human needs and their progression. According to Maslow, individuals are motivated by a series of needs that are organized in a hierarchical manner. The hierarchy consists of five levels, often depicted as a pyramid-shaped diagram.
Here is an explanation of each level of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs:
- Physiological Needs:
- At the base of the pyramid are the physiological needs, which are the most basic and essential needs for survival.
- These include necessities such as food, water, shelter, sleep, and other bodily requirements.
- Safety Needs:
- Once the physiological needs are met, individuals seek safety and security.
- This includes protection from physical harm, a stable and secure environment, employment security, financial security, and overall stability.
- Love and Belongingness Needs:
- Once the safety needs are satisfied, individuals seek social connection and a sense of belongingness.
- This level includes the need for love, affection, friendship, and intimacy.
- Esteem Needs:
- After fulfilling the love and belongingness needs, individuals strive for esteem needs.
- This level consists of two aspects: the need for self-esteem and the need for esteem from others.
- Self-Actualization Needs:
- At the top of the pyramid is the need for self-actualization, which represents the highest level of personal growth and fulfillment.
- Self-actualization refers to the desire to reach one's full potential, achieve personal goals, and engage in activities that bring a sense of purpose, meaning, and self-fulfillment.
Explain monetary policy, its objectives and tools.
Monetary policy is the process by which a central bank, such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), controls the supply of money and interest rates in an economy to achieve certain objectives. The objectives of monetary policy in India, as stated by the RBI, include:
- Price Stability:
- The primary objective is to maintain stable prices and control inflation. Price stability ensures the value of money remains steady, promoting economic activities, savings, investments, and employment.
- Exchange Rate Stability:
- The RBI aims to stabilize the external value of the Indian rupee over time. A stable exchange rate helps in maintaining competitiveness in international trade and minimizing volatility in import and export costs.
- High Economic Growth:
- Monetary policy plays a role in promoting sustained and high economic growth. By managing interest rates and money supply, the RBI aims to create a favorable environment for investment, productivity, and overall economic expansion.
- Controlled Expansion of Bank Credit:
- The RBI focuses on ensuring that bank credit and money supply expand in a controlled manner. This involves balancing the need for credit availability to support economic activities while avoiding excessive lending that could lead to financial instability.
- Promotion of Fixed Investment:
- Monetary policy aims to encourage productive investment by limiting non-essential fixed investment. This helps in directing resources towards sectors that contribute to long-term economic growth.
- Efficiency in the Financial System:
- The RBI strives to enhance the efficiency of the financial system by introducing structural changes, such as deregulating interest rates, improving credit delivery systems, and introducing new money market instruments. These measures promote a more competitive and flexible financial sector.
- Reducing Rigidity:
- The RBI aims to bring about flexibility in operations and promote a more competitive environment in the financial system. It seeks to reduce rigidities, encourage diversification, and maintain discipline and prudence in the functioning of the financial system.
To implement monetary policy, the RBI uses various tools, which can be classified as quantitative and qualitative tools:
Quantitative Tools (General Credit Control Tools):
- Repo Rate:
- Reverse Repo Rate:
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF):
- Bank Rate:
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR):
- Open Market Operations (OMOs):
Qualitative Tools(Selective Credit Control Tools):
- Moral Suasion:
- Persuasive measures used by the RBI to influence banks' lending behavior and credit allocation.
- Direct Credit Control:
- Imposing credit ceilings or restrictions on specific sectors or activities.
Explain in detail about various functions of banking.
Banking plays a crucial role in the economy by providing a wide range of financial services to individuals, businesses, and governments. The functions of banking can be categorized into the following key areas:
- Accepting Deposits:
- Banks accept deposits from individuals and businesses, providing a safe and convenient way to store money.
- Granting Loans and Advances:
- Banks provide loans and advances to borrowers, supporting various activities such as home loans, business loans, and personal loans.
- Credit Creation:
- Banks have the ability to create credit by extending loans, contributing to the expansion of the money supply and facilitating economic growth.
- Payment and Settlement System:
- Banks facilitate transactions and payments between individuals and businesses through services like check clearing, electronic fund transfers, and debit/credit cards.
- Foreign Exchange Services:
- Banks offer foreign exchange services, allowing customers to exchange currencies for international trade, travel, or investment.
- Investment and Wealth Management:
- Banks provide investment products and advisory services to help individuals and organizations grow and manage their financial assets.
- Safekeeping and Custodial Services:
- Banks offer secure storage solutions for valuable assets, documents, and securities, ensuring their safekeeping.
- Money Market Operations:
- Banks participate in money market operations by buying and selling short-term debt instruments, influencing liquidity and short-term interest rates.
- Advisory and Consultancy Services:
- Banks provide financial advisory and consultancy services on matters like investment strategies, risk management, and financial planning.
- Government Banking:
- Banks serve as bankers to governments, managing accounts, providing loans, and facilitating government transactions and public debt management.
Explain in brief Poverty (causes, types, and measure to eradicate).
Explain the causes of poverty in brief.(4 mark)
Poverty is a complex social issue characterized by a lack of sufficient income or resources to meet basic human needs. It is influenced by various factors and manifests in different forms. Here is a brief explanation of poverty, including its causes, types, and measures to eradicate it:
Causes of Poverty:
- Lack of Education and Skills:
- Limited access to quality education hinders individuals from acquiring the necessary knowledge and abilities for better job opportunities.
- Unemployment and Underemployment:
- Insufficient jobs and low wages contribute to income insecurity and poverty.
- Inequality and Discrimination:
- Income disparities and discrimination based on gender, race, or ethnicity contribute to persistent poverty.
- Economic Factors:
- Economic downturns and structural issues in the economy can lead to reduced job opportunities and income decline. Causes of poverty can vary, but here are some common factors:
- Environmental Factors:
- Natural disasters, climate change, and environmental degradation can disrupt livelihoods and exacerbate poverty.
- Poor Governance and Corruption:
- Weak governance, corruption, and mismanagement of resources can hinder economic development and perpetuate poverty.
- Health Issues:
- Geographical Factors:
- Discrimination and Inequality:
- Social Factors:
Types of Poverty:
- Absolute Poverty:
- Lack of essential resources for survival, such as food, water, shelter, and healthcare.
- Relative Poverty:
- Inability to afford the same level of goods and services as the majority of the population.
Measures to Eradicate Poverty:
- Education and Skill Development:
- Promoting quality education and skills training to enhance employment opportunities.
- Employment Generation:
- Fostering an environment that encourages job creation and entrepreneurship.
- Social Protection Programs:
- Implementing safety nets like cash transfers and subsidized healthcare.
- Addressing Inequality:
- Reducing income disparities and promoting social inclusion.
- Access to Basic Services:
- Ensuring access to healthcare, education, water, sanitation, and affordable housing.
- Sustainable Economic Development:
- Investing in infrastructure, agriculture, and industry to promote inclusive growth.
- Empowering Women:
- Promoting gender equality and women's empowerment to alleviate poverty.
List the type of Organization. Explain any one type in detail.
- Line Organisational
- Staff or Functional Authority Organisation
- Committee Organisation
- Matrix Organisational Structure
- Hybrid Organisational Structure
- Line and Staff Organisation
Among the different types of organizations listed, let's explore the Matrix Organizational Structure in detail.
Matrix Organizational Structure:
- The Matrix Organizational Structure is a hybrid form of organization that combines elements of both functional and project-based structures. In this structure, employees report to both functional managers (who are responsible for specific areas of expertise) and project managers (who oversee specific projects or initiatives).
Key Features:
- Dual Reporting Lines:
- Employees have two reporting lines: one to the functional manager and another to the project manager. The functional manager focuses on the employee's technical development and performance within their area of expertise, while the project manager oversees the employee's work on specific projects.
- Project-Based Teams:
- Project teams are formed to carry out specific tasks or projects. These teams are cross-functional and typically consist of employees from different departments or functional areas, allowing for a diverse range of skills and perspectives.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:
- The matrix structure enables organizations to respond quickly to changing demands and priorities. It allows for flexibility in resource allocation, as employees can be assigned to different projects based on their skills and availability.
Advantages of Matrix Organizational Structure:
- Efficient Resource Utilization:
- The matrix structure allows organizations to maximize the efficient use of resources by sharing personnel across projects.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
- The matrix structure encourages open communication and collaboration among employees from different functional areas.
- Improved Project Management:
- With dedicated project managers overseeing specific projects, there is better coordination, task assignment, and monitoring of project progress.
Disadvantages of Matrix Organizational Structure:
- Complexity and Conflicting Priorities:
- Employees may face challenges in managing conflicting priorities between functional and project managers.
- Increased Administrative Burden:
- The dual reporting structure requires additional administrative efforts to coordinate activities, potentially leading to increased bureaucracy.
- Potential for Power Struggles:
- Conflicts can arise between functional managers and project managers, leading to power struggles over resource allocation and decision-making authority.
Explain “Fiscal Policy”, write its objectives.
Explain fiscal policy, its objectives and tools.
Discuss the objectives of fiscal policy.(winter-4)
- Fiscal policy refers to the government's use of taxation and spending to influence the economy. It involves the government's decisions on how to raise revenue through taxes and how to allocate and spend that revenue.
- The objectives of fiscal policy can vary depending on the economic conditions and goals of the government. However, some common objectives include:
- Accelerate Economic Growth:
- Fiscal policy aims to achieve rapid economic growth and development by mobilizing financial resources and providing incentives to entrepreneurs.
- Efficient Allocation of Financial Resources:
- Fiscal policy ensures the effective allocation of resources for development activities and discourages socially undesirable goods.
- Employment Generation:
- Fiscal policy aims to generate employment through investments in infrastructure, support for small-scale industries, rural employment programs, and self-employment schemes.
- Price Stability and Control of Inflation:
- Fiscal policy aims to control inflation by reducing fiscal deficits, implementing tax-saving schemes, and utilizing financial resources productively.
- Equality of Income Distribution and Wealth:
- Fiscal policy aims to reduce income inequalities by implementing progressive taxation and investing in poverty alleviation programs.
- Capital Formation:
- Fiscal policy encourages savings and discourages excessive spending to increase the rate of capital formation and accelerate economic growth.
- Balanced Regional Development:
- Fiscal policy promotes balanced regional development through incentives for setting up projects in backward areas.
- Increasing National Income:
- Fiscal policy aims to increase the national income of a country through capital formation and economic growth.
- Foreign Exchange Earnings:
- Fiscal policy encourages exports and import substitution to earn foreign exchange and address balance of payments issues.
Tools of Fiscal Policy:
-
Public Expenditure: Managing the quantum of public expenditure within the scope of fiscal measures.
-
Public Debt: Ensuring that the volume of public debt remains within reasonable limits.
-
Taxation: Utilizing taxation as a tool for financing public expenditure and striking a balance between government needs and incentives for income generation.
Explain in detail about various methods of computing national income.
- National income refers to the monetary value over a period of time of the output flow of goods and services produced in an economy.
- The Uses of National Income Statistics Measuring the level and rate of growth of national income (Y) is essential to keep track of:
- The rate of economic growth
- Changes to living standards
- Changes to the distribution of income b/w groups
-
Product Method or Value-Added Method:
- This method calculates national income by determining the monetary value of all final goods and services produced within an economy over a specific period.
- It avoids double counting by focusing on the value-added at each stage of production and excluding intermediate goods.
- Formula: NNPfc = GDPmp – Depreciation – Net indirect taxes + NFIA, OR,
- NNPfc = GDPmp – Depreciation – Net product taxes – Net production taxes + NFIA
-
Income Method:
- The income method calculates national income by summing up the factor incomes earned by individuals involved in production.
- It includes wages, salaries, rent, interest, profit, and mixed income.
- Formula: National Income = Rent + Compensation + Interest + Profit + Mixed Income.
-
Expenditure Method:
- The expenditure method calculates national income by considering the total spending on final goods and services within an economy.
- It includes household consumption, government expenditure, investment expense, and net exports.
- Formula: National Income: Household Consumption + Government Expenditure + Investment expense + Net Export (Exports – Imports) -NNPfc = C + G + I + NX.
Explain the term Unemployment, its types, causes and remedies.
Unemployment is when people who want to work can't find suitable jobs. It's a big problem that affects individuals, families, and society as a whole. It can lead to financial struggles, poor mental health, and a lower quality of life.
There are different Types of unemployment:
-
Frictional Unemployment: This happens when people are between jobs or looking for their first job. It's temporary and normal.
-
Structural Unemployment: This occurs when people's skills don't match the jobs available. It happens when technology changes, industries shift, or skills become outdated.
-
Cyclical Unemployment: This is linked to the ups and downs of the economy. During recessions, there's less demand for goods and services, so fewer jobs are available. When the economy grows, unemployment decreases.
-
Seasonal Unemployment: Some jobs are only available during certain times of the year, like in tourism or agriculture. People in these jobs are unemployed during off-seasons.
Unemployment can be Caused by:
-
Economic downturns: When the economy is weak, companies may cut jobs or stop hiring.
-
Technological advancements: New technology can make certain jobs unnecessary, leading to unemployment.
-
Lack of education and skills: If people don't have the right education or skills for available jobs, they may struggle to find work.
-
Labor market factors: Things like wages, labor regulations, and job matching efficiency can affect unemployment rates.
To tackle unemployment, we can:
-
Improve education and skill development: By investing in education and training programs, people can acquire the skills needed for available jobs.
-
Stimulate economic growth: Governments can promote growth by investing in infrastructure, offering tax incentives to businesses, and supporting key industries. This creates more jobs.
-
Reform the labor market: Making labor markets more flexible, reducing barriers to entry, and improving job matching mechanisms can help reduce unemployment. This includes reducing restrictive labor regulations and encouraging innovation.
-
Provide social safety nets: Establishing programs like unemployment benefits and job placement services can offer temporary support to unemployed individuals and help them find work.
-
Support entrepreneurship and small businesses: Encouraging people to start their own businesses can lead to job creation and more opportunities.
What are the principles of organizational structures? Elaborate in details.
- Organizational structure refers to the framework or system through which an organization arranges its activities, resources, and relationships to achieve its goals effectively.
- It encompasses the distribution of tasks, responsibilities, and authority within the organization. There are several principles that underlie effective organizational structures.
- Organizational structure is how an organization arranges its activities, resources, and relationships to achieve its goals effectively.
-
Division of Labor: Breaking down work into specific tasks and assigning them to individuals or groups improves efficiency and specialization.
-
Hierarchy: Establishing levels of authority and responsibility clarifies reporting relationships and decision-making processes.
-
Span of Control: The number of subordinates a manager supervises affects coordination and communication.
-
Unity of Command: Employees should have one direct supervisor to avoid confusion and maintain clear lines of authority.
-
Centralization and Decentralization: Deciding whether decision-making is concentrated at the top or distributed to lower levels depends on organizational needs.
-
Formalization: The level of documented rules and procedures affects consistency and control.
-
Departmentalization: Grouping activities and individuals based on functions, products, geography, or customers improves coordination and specialization.
-
Coordination: Integrating activities, sharing information, and aligning efforts across departments ensures collaboration and goal achievement.
Explain Corporate Social Responsibility of a Multinational organization.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is when a multinational organization voluntarily takes actions to operate ethically and sustainably, considering the interests of employees, customers, communities, and the environment.
-
Ethical Business Practices: MNCs follow laws, promote fairness, integrity, and transparency, and avoid harmful practices.
-
Environmental Sustainability: MNCs reduce their environmental impact by conserving resources, minimizing pollution, using renewable energy, and managing waste responsibly.
-
Employee Welfare: MNCs prioritize employee well-being, offering safe conditions, fair pay, equal opportunities, training, diversity, work-life balance, and health and safety support.
-
Community Engagement: MNCs support community development through initiatives like education, healthcare, infrastructure, philanthropy, and employee volunteering.
-
Supply Chain Responsibility: MNCs ensure ethical practices in their supply chains, including fair labor conditions, human rights, and regular audits.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: MNCs engage stakeholders through dialogue, feedback, and involving them in decision-making to build trust, manage risks, and create shared value.
-
Ethical Marketing and Consumer Protection: MNCs market honestly, provide accurate product information, respect consumer rights, prioritize safety, quality, and responsible innovation.
-
Global Social Impact: MNCs address global challenges like poverty, inequality, and climate change through initiatives like poverty alleviation, education, healthcare, and environmental conservation.
Corporate Social Responsibility must be made compulsory for all organizations. Give your comments for the same, and also give good examples of it.
The idea of making CSR compulsory for all organizations is a topic of debate. Here are some key points to consider:
Benefits of Making CSR Compulsory:
- It ensures that organizations are held accountable for their social and environmental impact, promoting ethical practices.
- Mandatory CSR can drive organizations to adopt sustainable practices and make positive contributions to society and the environment.
- It creates a level playing field, as all organizations would be equally responsible for their societal impact.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Making CSR compulsory may impose additional compliance requirements and costs, particularly for smaller organizations that may struggle with the resources needed.
- Voluntary CSR allows organizations to tailor their initiatives to their specific contexts and encourages flexibility and innovation, which may be limited by mandatory requirements.
- Effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms would be necessary to ensure compliance with mandatory CSR.
Examples of Good CSR Initiatives:
- Patagonia, an outdoor clothing company, promotes environmental sustainability, fair trade, and donates a portion of its revenue to environmental causes.
- Microsoft's "AI for Good" initiative uses artificial intelligence to address societal challenges such as healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability.
- Unilever's Sustainable Living Plan focuses on reducing environmental impact, improving hygiene and nutrition, and enhancing livelihoods in communities where it operates.
- Google invests in renewable energy, aims for zero waste, and supports initiatives for education and economic opportunity.